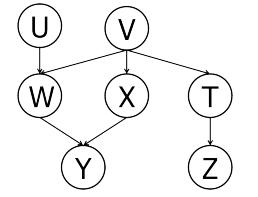
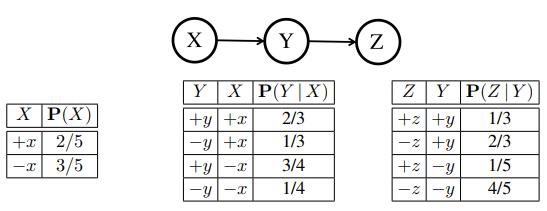
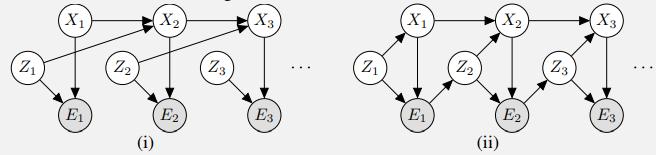
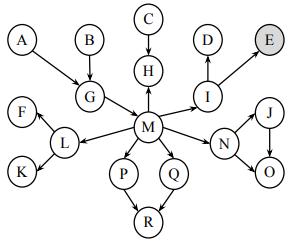
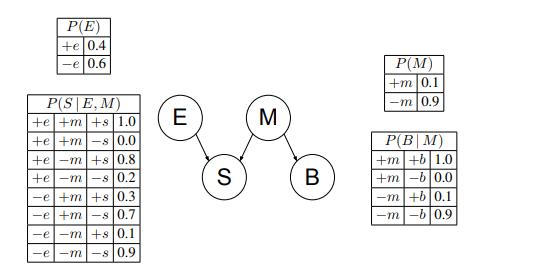
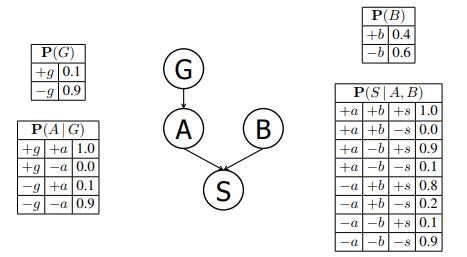
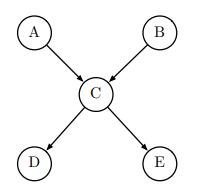
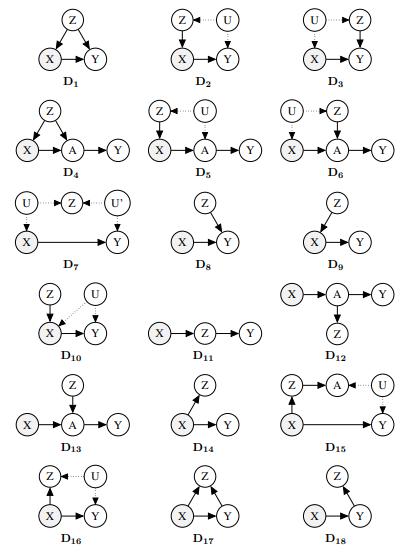
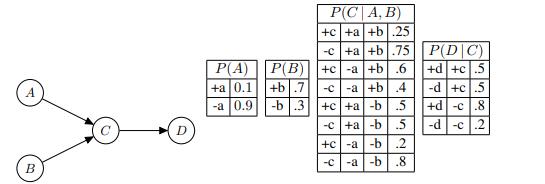
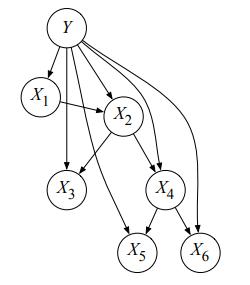
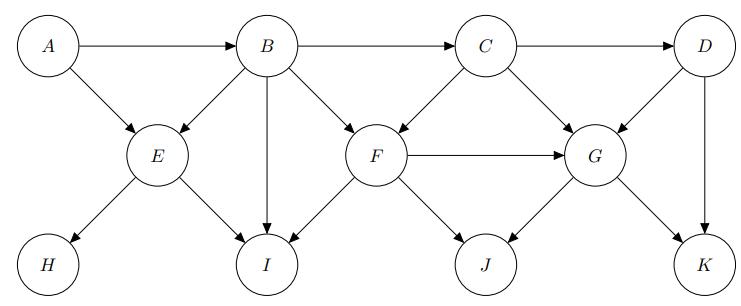
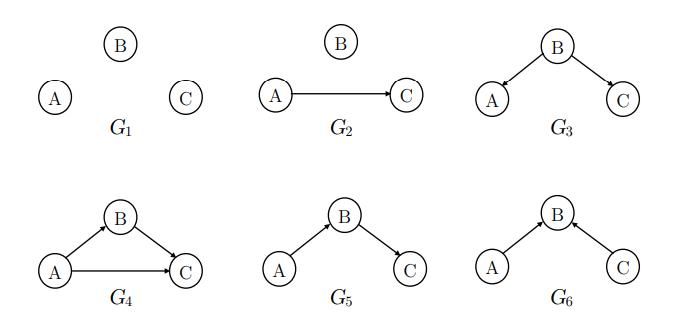
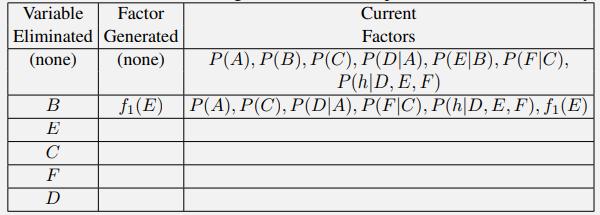
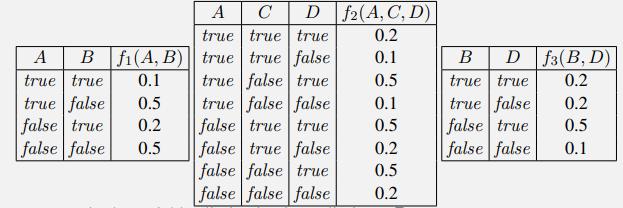
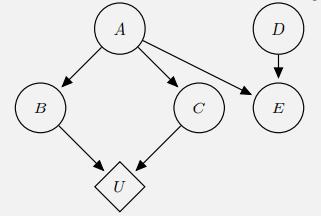
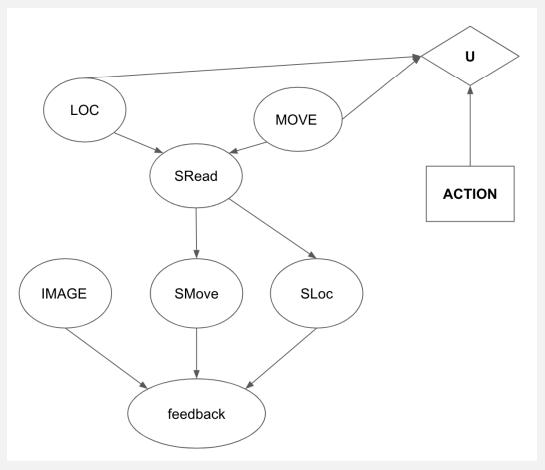
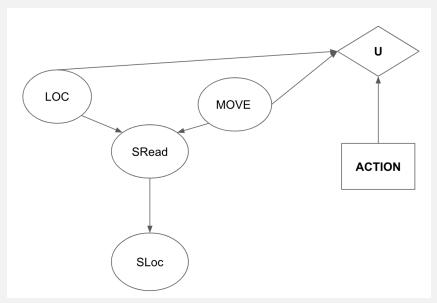
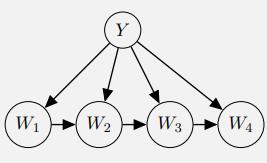
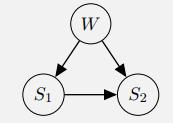
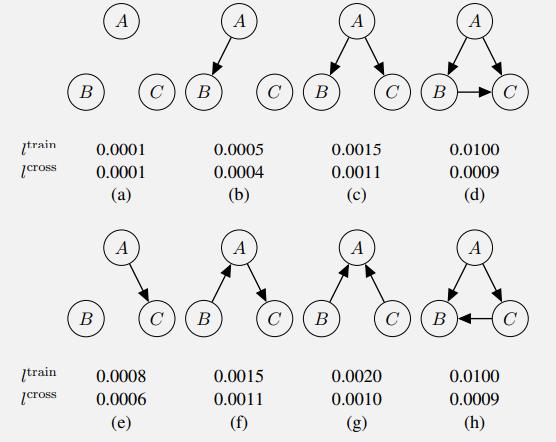
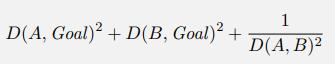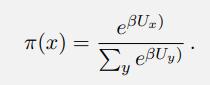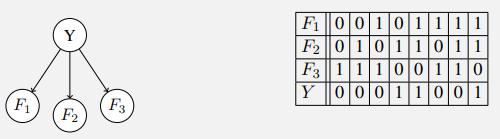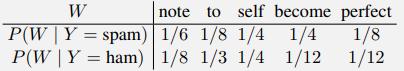Artificial Intelligence A Modern Approach 4th Edition Stuart Russell, Peter Norvig - Solutions
Discover comprehensive solutions and answers for "Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 4th Edition" by Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig. Access our online answers key and solutions manual to enhance your understanding of this essential textbook. With detailed chapter solutions and a test bank, our platform provides step-by-step answers to solved problems, making complex concepts easy to grasp. Whether you're looking for a solution manual, instructor manual, or a free download of the solutions PDF, we offer all the resources you need for effective learning. Explore the questions and answers section to navigate the intricacies of AI effortlessly.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()