Consider the simple bimolecular reaction A + B C + D, where k +1 and k -1
Question:
Consider the simple bimolecular reaction A + B ![]() C + D, where k+1 and k-1 are the rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions. ΔG is related to the concentration of the reactants and products as well as the equilibrium constant, K, as described by Equation 3.27:
C + D, where k+1 and k-1 are the rate constants for the forward and reverse reactions. ΔG is related to the concentration of the reactants and products as well as the equilibrium constant, K, as described by Equation 3.27:
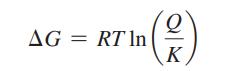
Since the law of mass action governs reaction kinetics, the forward and reverse fluxes, J, can be defined as:
J+ = k+1 [A] [B] (forward flux); J- = k-1 3 [C] [D] (reverse flux)
ΔG can be defined in terms of the ratio of forward and reverse fluxes:
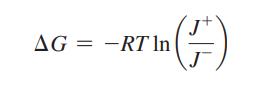 Derive this equation.
Derive this equation.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Biochemistry Concepts And Connections
ISBN: 9780134641621
2nd Edition
Authors: Dean Appling, Spencer Anthony-Cahill, Christopher Mathews
Question Posted:





