Introduction To Actuarial And Financial Mathematical Methods 1st Edition Stephen Garrett - Solutions
Unlock the comprehensive solutions to "Introduction to Actuarial and Financial Mathematical Methods" by Stephen Garrett with our extensive resources. Discover online answers key and solutions pdf that provide step-by-step answers to all your queries. Our solution manual offers a detailed guide to solved problems, ensuring you grasp each concept thoroughly. Access the test bank for challenging questions and answers, while the instructor manual provides chapter solutions tailored for effective learning. Enhance your understanding with our textbook aids, available for free download. Dive into this wealth of knowledge and master actuarial and financial mathematics today.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()



![a. A = b. B = 4] 4 1 c. C = [-2 -1 3 8 2] 14 25 36 c. D= -2 -4 -3 1 2 3 2 132 231 312 021 007](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/0/5/251657410a33d1561702105249800.jpg)
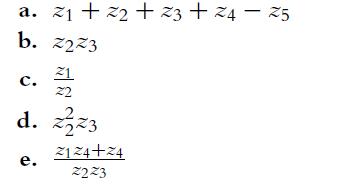
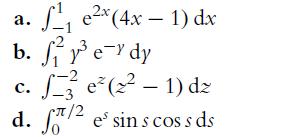
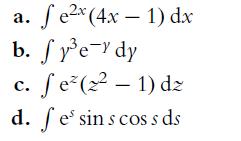


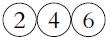

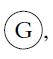
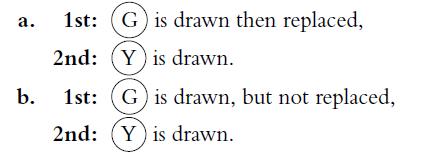
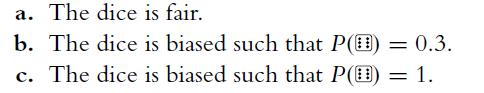
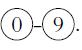
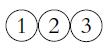
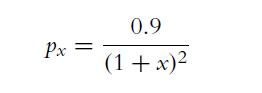
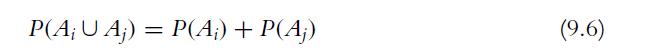
![P(A) [0, 1] P() = 1 - P(0) = 0 - (9.3) (9.4) (9.5)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/0/3/9/6496573106123c1e1702039646029.jpg)

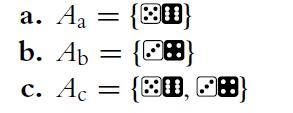
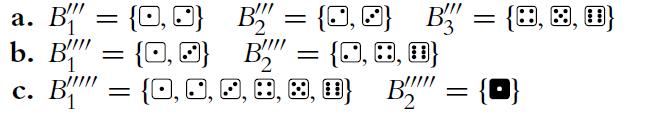

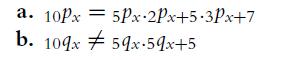
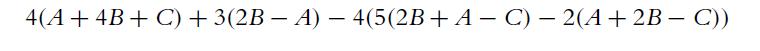
![4 4 -11 3 1-1 a. A = b. C = c. E = B = 121 254 4 3 1 -1 4 1 12 121 [134]). D=[#] 23 23 14 121 F= * = [24]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/0/5/261657410adbd25d1702105259921.jpg)
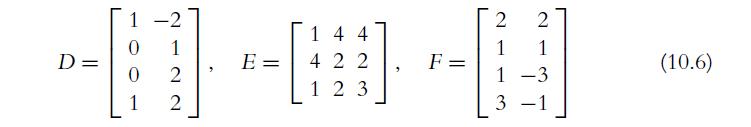
![a. b. 2 2(BT-21)- = [i-1] 2 1 (BT-212) = [81] 0](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/1/0/190657423ee84eb91702110189200.jpg)

![A 12 [121 2] 21 -[ and B = 01 32](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/0/5/327657410ef7e6251702105325829.jpg)
![C= [0 153], D= 1 4 -1 2 -3 R= [2]. E F=[01]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/0/5/4026574113ad6bb31702105400747.jpg)
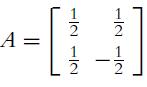
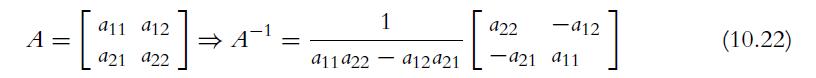
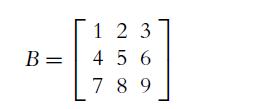
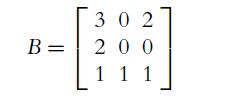
![C(D) = [cij (D)] = 2 3 0 2 -4 3 -3 -3 -3 3 3 -1 -3 -1 3 5 (10.29)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/0/6/5226574159adfa951702106520162.jpg)
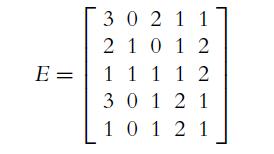
![2C- - [ {]-[ 12 -1 2 10 4 5 -5 - 2C](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/0/6/581657415d58cadb1702106579252.jpg)
![02 T (4-[4-7]) = 24-[69] AT 10 2A -1 01](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/0/6/601657415e9e4fb41702106599060.jpg)
![01 23 a. (B-)T [ ] b. (28-1) = [12] T 10 (HD)-[R] B 1 1 C. 10 21 12 10 21 d. ([1])" - [2] B 12](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/0/6/62765741603255b51702106624790.jpg)
![00 +4[83]-[1] 03 a. 2A + A 12 00 12 +[89] B= [1] [03 b. 2B+](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/1/0/6/612657415f4954871702106610247.jpg)