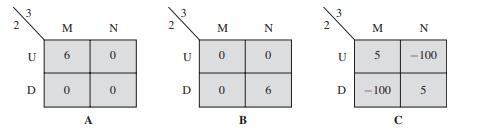
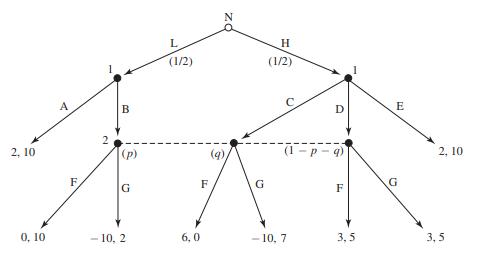
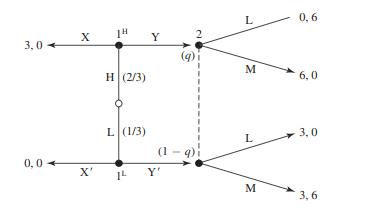
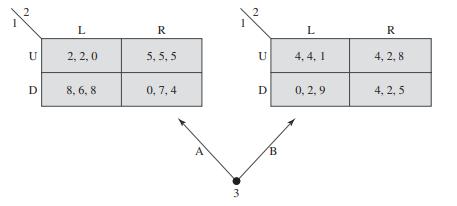
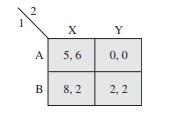
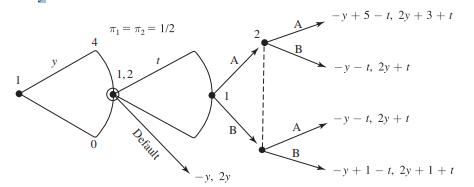
Strategy An Introduction To Game Theory 3rd Edition Joel Watson - Solutions
Unlock the full potential of your understanding with our comprehensive solutions to "Strategy: An Introduction to Game Theory, 3rd Edition" by Joel Watson. Access online answers key and detailed solutions manual, perfect for tackling solved problems and exploring chapter solutions. Our step-by-step answers provide clarity, while the test bank and instructor manual enhance your learning experience. Whether you're looking for textbook insights or free download options, our solutions PDF ensures you have all the questions and answers at your fingertips. Dive into a world of strategic thinking with this essential guide.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()