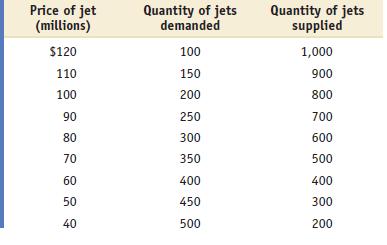
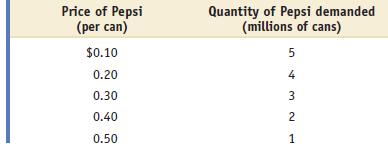
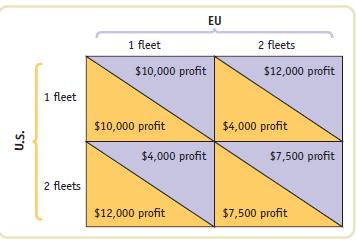
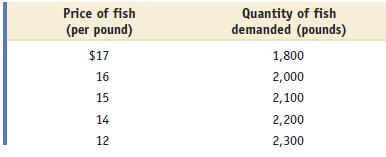
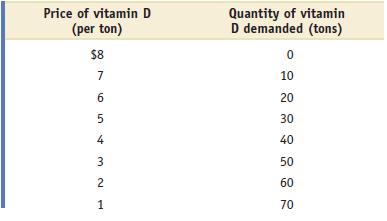
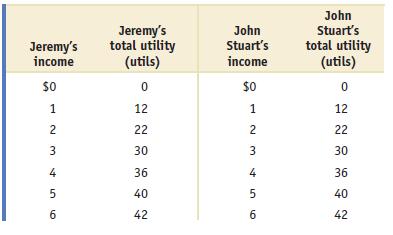
Microeconomics 1st Edition Paul Krugman, Robin Wells - Solutions
Unlock the potential of your economics studies with our comprehensive resources for "Microeconomics 1st Edition" by Paul Krugman and Robin Wells. Access step-by-step answers and solution manuals online, providing clear guidance through complex problems. Discover a complete answers key, solutions PDF, and solved problems tailored to each chapter. Our instructor manual and test bank offer extensive questions and answers, enhancing your understanding and preparation. Whether you're seeking chapter solutions or a textbook companion, enjoy free downloads that simplify your learning journey. Elevate your microeconomics knowledge with our expertly crafted educational tools.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()