Rating funny cartoons. Newspaper cartoons, although designed to be funny, often invoke hostility, pain, or aggression in
Question:
Rating funny cartoons. Newspaper cartoons, although designed to be funny, often invoke hostility, pain, or aggression in readers, especially when those cartoons depict violence. A study was undertaken to determine how violence in cartoons is related to aggression or pain
(Motivation and Emotion, Vol. 10, 1986). A group of volunteers
(psychology students) rated each of 32 violent newspaper cartoons (16 “Herman” and 16 “Far Side”
cartoons) on three dimensions: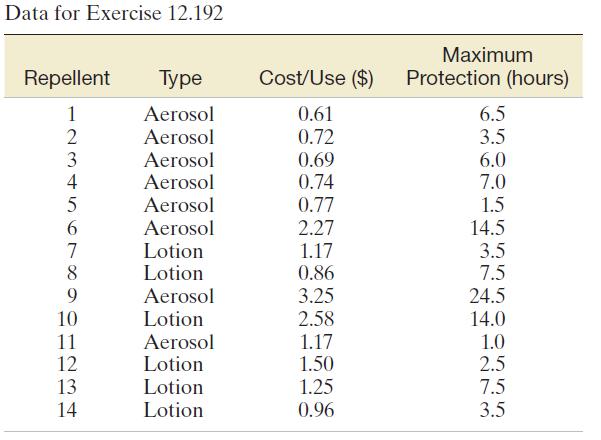
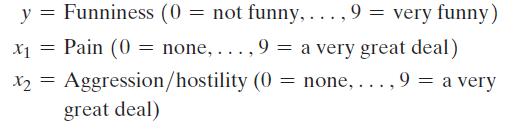
The ratings of the students on each dimension were averaged, and the resulting n = 32 observations were subjected to a multiple-regression analysis. On the basis of the underlying theory (called the inverted-U theory) that the funniness of a joke will increase at low levels of aggression or pain, level off, and then decrease at high levels of aggression or pain, the following quadratic models were proposed:
Model 1: E1y2 = b0 + b1 x1 + b2 x1 2 , R2 = .099, F = 1.60 Model 2: E1y2 = b0 + b1 x2 + b2 x2 2 , R2 = .100, F = 1.61
a. According to the theory, what is the expected sign of b2 in each model?
b. Is there sufficient evidence to indicate that the quadratic model relating pain to funniness rating is useful?
Test at a = .05.
c. Is there sufficient evidence to indicate that the quadratic model relating aggression/hostility to funniness rating is useful? Test at a = .05.
Step by Step Answer:

Statistics Plus New Mylab Statistics With Pearson Etext Access Card Package
ISBN: 978-0134090436
13th Edition
Authors: James Mcclave ,Terry Sincich






