Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the surface integral S F ds; that is, calculate
Question:
Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the surface integral ∫∫S F · ds; that is, calculate the flux of F across S.
F(x, y, z) = x2yi + xy2j + 2xyzk, S is the surface of the tetrahedron bounded by the planes x = 0, y = 0, z = 0, and x + 2y + z = 2
Data from the Divergence Theorem
Let E be a simple solid region and let S be the boundary surface of E, given with positive (outward) orientation. Let F be a vector field whose component functions have continuous partial derivatives on an open region that contains E. Then
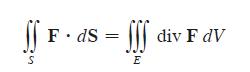
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





