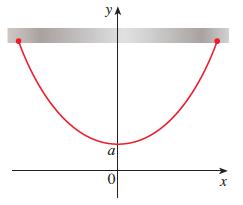
Catenary Curves A chain (or cable) of uniform density that is suspended between two points, as shown
Question:
Catenary Curves A chain (or cable) of uniform density that is suspended between two points, as shown in the figure, hangs in the shape of a curve called a catenary with equation y = a cosh(x/a).
The British physicist and architect Robert Hooke (1635–1703) was the first to observe that the ideal shape for a free standing arch is an inverted catenary. Hooke remarked, “As hangs the chain, so stands the arch.” The Gateway Arch in St. Louis is based on the shape of a catenary; the central curve of the arch is modeled by the equation
y = 211.49 – 20.96 cosh 0.03291765x
where x and y are measured in meters and |x| ≤ 91.20. Set up an integral for the length of the arch and evaluate the integral numerically to estimate the length correct to the nearest meter.
Step by Step Answer:

Calculus Early Transcendentals
ISBN: 9781337613927
9th Edition
Authors: James Stewart, Daniel K. Clegg, Saleem Watson, Lothar Redlin





