This is a velocitytime graph for a vertically bouncing ball. The ball is released at A and
Question:
This is a velocity–time graph for a vertically bouncing ball.
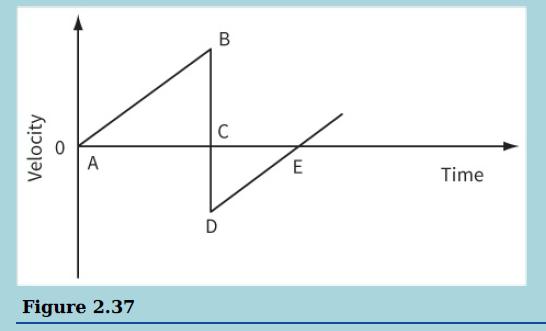
The ball is released at A and strikes the ground at B. The ball leaves the ground at D and reaches its maximum height at E. The effects of air resistance can be neglected.
a. State:
i. Why the velocity at D is negative
ii. Why the gradient of the line AB is the same as the gradient of line DE
iii. What is represented by the area between the line AB and the time axis
iv. Why the area of triangle ABC is greater than the area of triangle CDE.
b. The ball is dropped from rest from an initial height of 1.2 m. After hitting the ground the ball rebounds to a height of 0.80 m. The ball is in contact with the ground between B and D for a time of 0.16 s.
Using the acceleration of free fall, calculate:
i. The speed of the ball immediately before hitting the ground
ii. The speed of the ball immediately after hitting the ground
iii. The acceleration of the ball while it is in contact with the ground. State the direction of this acceleration.
Step by Step Answer:

Cambridge International AS And A Level Physics Coursebook
ISBN: 9781108859035
3rd Edition
Authors: David Sang, Graham Jones, Gurinder Chadha, Richard Woodside





