Hydrogen, iodine and hydrogen iodide are in equilibrium in a sealed tube at constant temperature. The equation
Question:
Hydrogen, iodine and hydrogen iodide are in equilibrium in a sealed tube at constant temperature. The equation for the reaction is:
H2 + I2 ⇋ 2HI(g) ΔHr = –96 kJ mol–1
The partial pressures of each gas are shown in the table below.
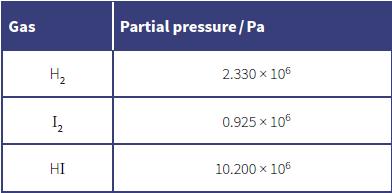
a. Explain the meaning of the term partial pressure.
b. Calculate the total pressure of the three gases in this mixture.
c. Write an equilibrium expression for this reaction in terms of partial pressures.
d. Calculate a value for Kp for this reaction, including the units.
e. Use Le Chatelier’s principle to explain what happens to the position of equilibrium in this reaction when:
i. The temperature is increased
ii. Some iodine is removed.
Step by Step Answer:

Cambridge International AS And A Level Chemistry Coursebook
ISBN: 9781316637739
2nd Edition
Authors: Lawrie Ryan, Roger Norris





