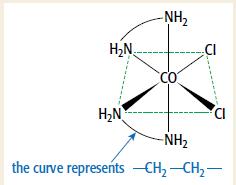
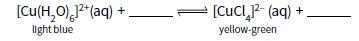
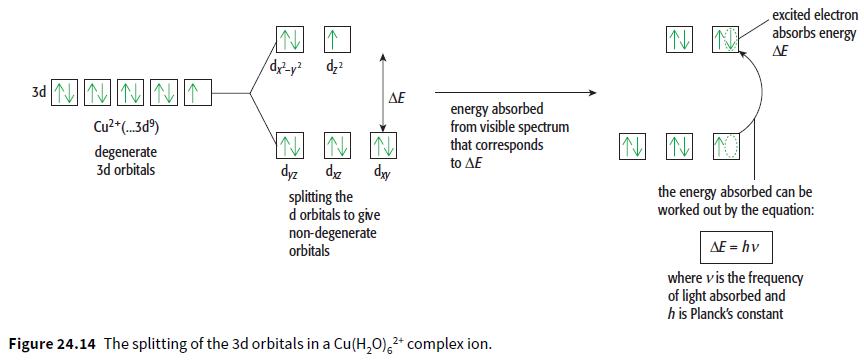
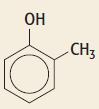
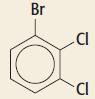
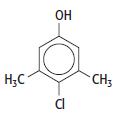
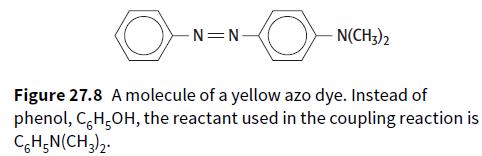
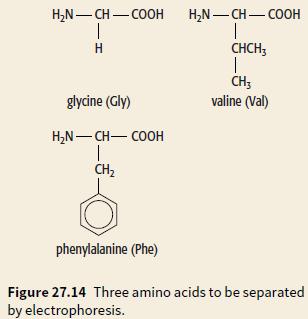
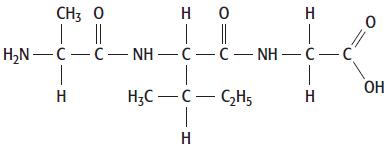
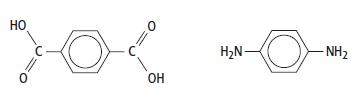
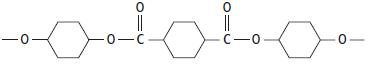
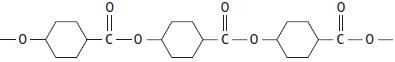
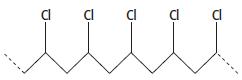
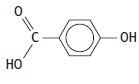
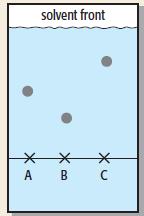
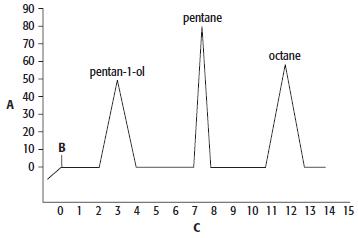
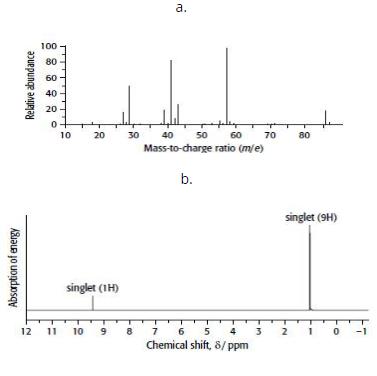
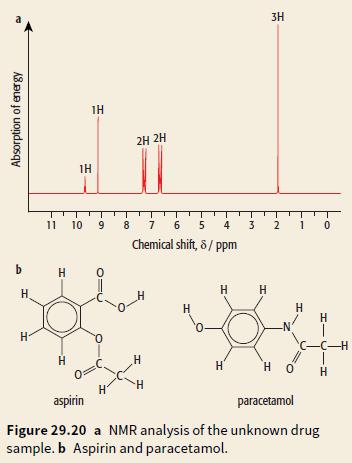
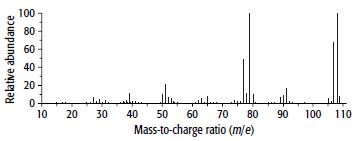
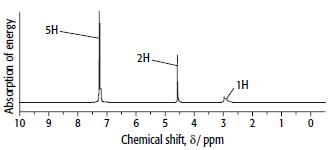
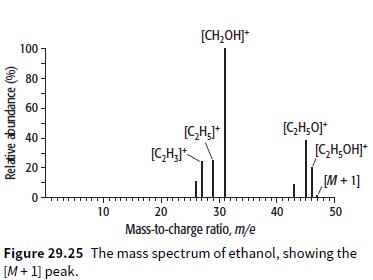
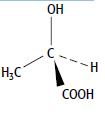
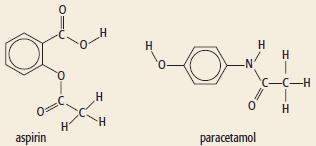
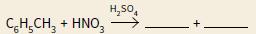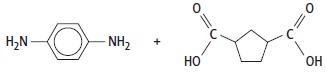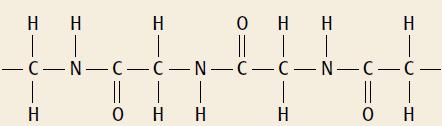Cambridge International AS And A Level Chemistry Coursebook 2nd Edition Lawrie Ryan, Roger Norris - Solutions
Unlock the potential of your chemistry studies with our comprehensive solutions for the "Cambridge International AS and A Level Chemistry Coursebook 2nd Edition" by Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris. Access our online answers key and solutions manual to gain insights into solved problems and step-by-step answers. Enhance your understanding with our free downloadable solutions PDF, featuring questions and answers tailored for effective learning. Benefit from the instructor manual and test bank to excel in your chemistry journey. Dive into detailed chapter solutions and explore the textbook content with ease, all available for free download today!
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()