The list below gives the standard electrode potentials for five half-reactions. Cu 2+ (aq) + e
Question:
The list below gives the standard electrode potentials for five half-reactions.
Cu2+(aq) + e– Cu(s) Eθ= +0.34 V
Fe2+(aq) + 2e– → Fe(s) Eθ = –0.44 V
Fe3+(aq) + e– → Fe2+(aq) Eθ = +0.77 V
I2(aq) + 2e– → 2I–(aq) Eθ = +0.54 V
Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s) Eθ = –0.76 V
a. What is the meaning of standard electrode potential? [
b Which species in the list is:
i. The strongest oxidising agent?
ii. The strongest reducing agent?
c. A cell was set up as shown below.
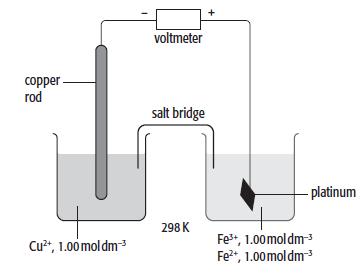
i. Calculate the standard cell potential of this cell.
ii. In which direction do the electrons flow in the external circuit? Explain your answer.
iii. Write an equation for the complete cell reaction.
d. The concentration of copper(II) ions in the left-hand electrode was increased from 1.00 mol dm–3 to 1.30 mol dm–3. The concentration of ions in the right-hand cell was not changed.
i. What effect does this change have on the E value of the Cu2+/Cu half-cell?
ii. What effect does this change have on the E value for the complete electrochemical cell?
iii. Why is the direction of the cell reaction unlikely to be altered by this change in concentration?
e. Lithium–iodine button cells are often used to power watches. Suggest two reasons, other than size, why button cells are used to power watches rather than ordinary ‘dry cells’.
Step by Step Answer:

Cambridge International AS And A Level Chemistry Coursebook
ISBN: 9781316637739
2nd Edition
Authors: Lawrie Ryan, Roger Norris




