Extract (p)-xylene and o-xylene from (n)-hexane diluent using (beta, beta^{prime}) thiodipropionitrile as solvent. Solvent and diluent can
Question:
Extract \(p\)-xylene and o-xylene from \(n\)-hexane diluent using \(\beta, \beta^{\prime}\) thiodipropionitrile as solvent. Solvent and diluent can be assumed to be immiscible. Feed rate is \(1000.0 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{h}\). The feed contains \(0.3 \mathrm{wt} \% \mathrm{p}-\) xylene and \(0.5 \mathrm{wt} \%\) o-xylene in n-hexane. We desire at least a \(90 \%\) recovery of p-xylene and at least \(95 \%\) recovery of o-xylene. Entering solvent is pure. Operation is at \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), and equilibrium data are in Problem 13.D15. Use a simple countercurrent cascade.
a. Calculate value of \((\mathrm{R} / \mathrm{E})_{\max }\) for both p-xylene and for o-xylene to just meet recovery requirements.
b. The smaller \((\mathrm{R} / \mathrm{E})_{\max }\) value represents the controlling or key solute. Operate at \(\mathrm{E}=1.5(\mathrm{E})_{\text {min,controlling. }}\). Find number of stages and solvent inlet flow rate.
c. Determine outlet raffinate concentration and percent recovery noncontrolling solute.
Problem 13.D15
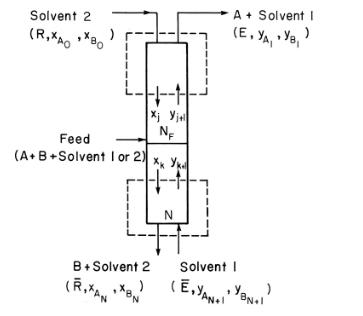
A liquid feed that is \(48 \mathrm{wt} \% \mathrm{~m}\)-xylene and \(52 \mathrm{wt} \%\) o-xylene is separated in a fractional extractor (Figure \(13-5\) ) at \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and \(101.3 \mathrm{kPa}\). Solvent 1 is \(\beta, \beta^{\prime}\)-thiodipropionitrile, and solvent 2 (diluent) is \(\mathrm{n}\) hexane. Equilibrium data are \(\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{d}, \mathrm{m}-\mathrm{xy}}=0.050\) and \(\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{d}, \mathrm{o}-\mathrm{xy}}=0.150\) where \(\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{d}, \mathrm{A}}=\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{A}}\) (in solvent) \(/ \mathrm{x}_{\mathrm{A}}\) (in diluent) (Perry and Green, 1984). For each kilogram of feed, \(200 \mathrm{~kg}\) of solvent 1 and \(20 \mathrm{~kg}\) of solvent 2 are used. Both solvents are pure when they enter the cascade. We desire a \(92 \%\) or better recovery of o-xylene in solvent 1 and a \(94 \%\) or better recovery of \(\mathrm{m}\)-xylene in \(\mathrm{n}\)-hexane. Use integer values of \(\mathrm{N}\) and \(\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{F}}\). Find outlet recoveries, solvent-free compositions, \(\mathrm{N}\), and \(\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{F}}\).
Figure 13-5
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





