Water at (60^{circ} mathrm{C}) and 0.95 bar is evaporating into a (12.0 mathrm{~cm}-1) ong tube (also at
Question:
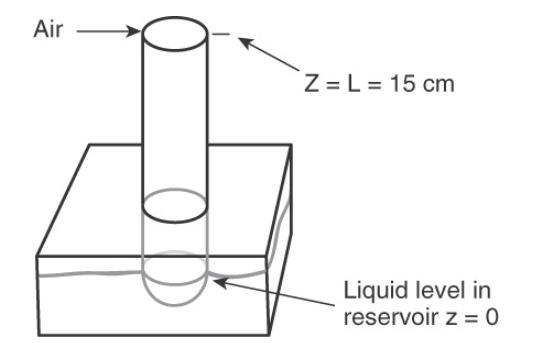
Water at \(60^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and 0.95 bar is evaporating into a \(12.0 \mathrm{~cm}-1\) ong tube (also at \(60^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) ) and diffusing through a stagnant layer of air. The device is illustrated in Figure 15-2.
a. Calculate the flux of water vapor if convection is included.
b. Calculate the value of the molar reference velocity.
c. If the tube is \(1.5 \mathrm{~cm}\) in diameter, calculate the grams of water evaporated per hour.
d. Calculate flux of water vapor if convection is not included (a calculation that is expected to be incorrect for this example).
Data: At \(60^{\circ} \mathrm{C}, D_{\text {water-air }}=3.05 \times 10^{-5} \mathrm{~m}^{2} / \mathrm{s}, \mathrm{VP}_{\text {water }}=149.5 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\)
Figure 15-2
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





