(a) Wolfram and Python 1. Vary B and observe the change in reaction rate. Go to...
Question:
(a) Wolfram and Python
1. Vary ΘB and observe the change in reaction rate. Go to the extremes and explain what is causing the curve to change the way it does.
2. Vary the parameters and list the parameters that have the greatest and the least effect on the reaction rate.
3. Write a set of conclusions about the experiments you carried out by varying the sliders in parts (i) through (iii). Polymath
4. Using the molar flow rate of SO2 (A) of 3 mol/h and calculate the fluidized bed (i.e., CSTR catalyst weight) necessary for 40% conversion.
5. Next, consider the entering flow rate of SO2 is 1000 mol/h. Plot (FA0/–rA) as a function of X to determine the fluidized bed catalyst weight necessary to achieve 30% conversion, and 99% of the equilibrium conversion, that is, X = 0.99 Xe.
(b) 1. Using Figure E4-5.1 and the methods in Chapter 2, estimate the PFR volume for 40% conversion for a molar flow rate of A of 5 dm3/min.
2. Using Figure E4-5.1 and the methods in Chapter 2, estimate the time to achieve 40% conversion in a batch reactor when the initial concentration is 0.05 mol/dm3. Wolfram and Python
3. What values of KC and CA0 cause Xef to be the farthest away from Xeb?
4. What values of KC and CA0 will cause Xeb and Xef to be the closest together?
5. Observe the plot of the ratio of (XebXer) as a function of yA0. Vary the values of KC and CT0. What conclusions can you draw?
6. Write a set of conclusions from your experiment (i) through (vi).
Figure E4-5.1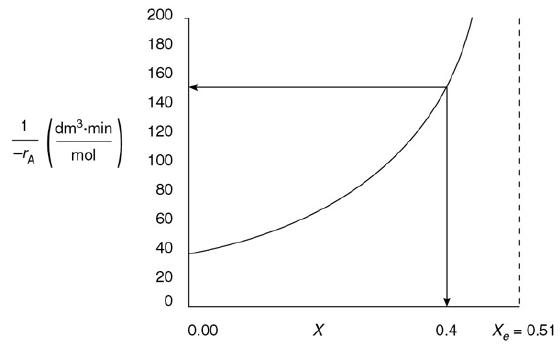
Step by Step Answer:






