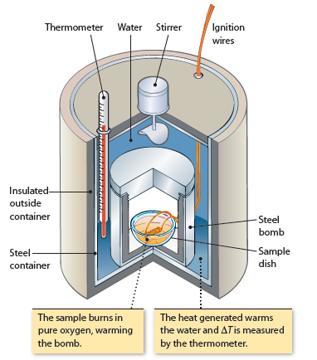
A 1.50 L constant-volume calorimeter (Figure 5.12) contains C 3 H 8 (g) and O 2 (g).
Question:
A 1.50 L constant-volume calorimeter (Figure 5.12) contains C3H8(g) and O2(g). The partial pressure of C3H8 is 0.10 atm and the partial pressure of O2 is 5.0 atm. The temperature is 20.0°C. A reaction occurs between the two compounds, forming CO2(g) and H2O(ℓ). The heat from the reaction causes the temperature to rise to 23.2°C.
(a) Write a balanced chemical equation for there action.
(b) How many moles of C3H8(g) are present in the flask initially?
(c) What is the mole fraction of C3H8(g) in the flask before reaction?
(d) After the reaction, the flask contains excess oxygen and the products of the reaction,CO2(g) and H2O(ℓ). What amount of unreacted O2(g) remains?
(e) After the reaction, what is the partial pressure exerted by the CO2(g) in this system?
(f) What is the partial pressure exerted by the excess oxygen remaining after the reaction?
Figure 5.12
Step by Step Answer:

Chemistry And Chemical Reactivity
ISBN: 9780357001172
10th Edition
Authors: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel





