The equilibrium constant for the reaction of formic acid and sodium hydroxide is 1.8 10 10
Question:
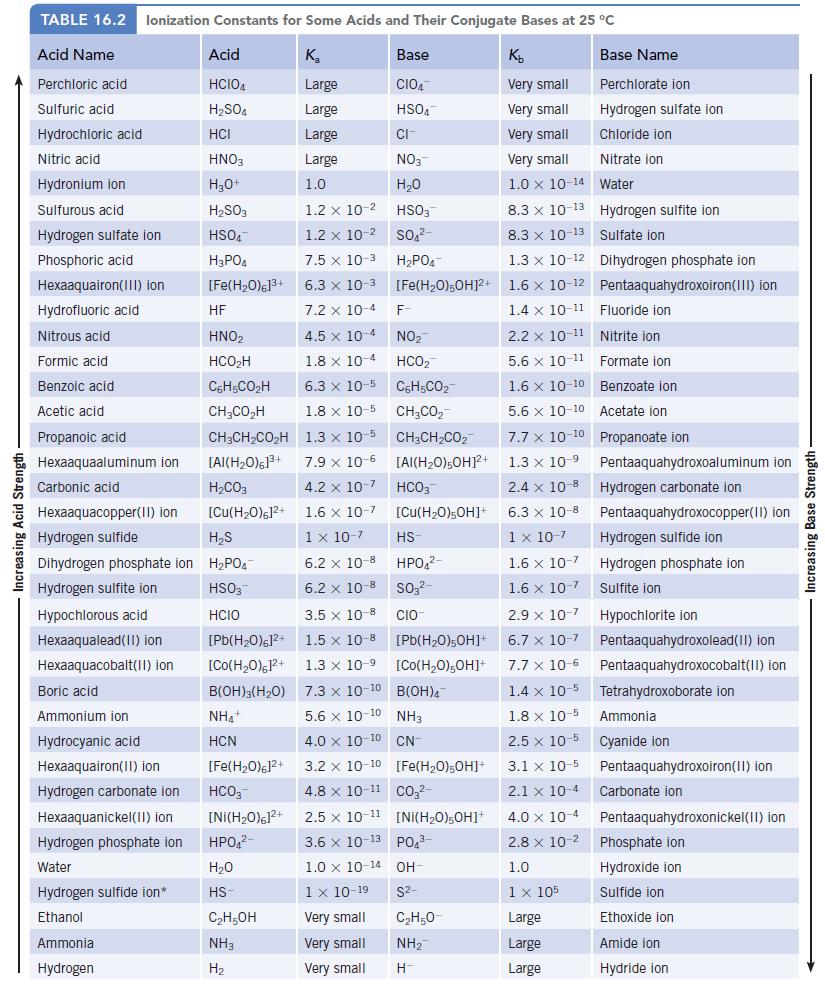
The equilibrium constant for the reaction of formic acid and sodium hydroxide is 1.8 × 1010 (page 726). Confirm this value.
Data given on Page 726
Consider the reaction of the naturally occurring weak acid formic acid, HCO2H, with sodium hydroxide. The net ionic equation is![]()
In this reaction, OH− is a much stronger base than HCO2− (Kb = 5.6 × 10−11), and the reaction is predicted to proceed to the right. If equal amounts of weak acid and base are mixed, the final solution will contain sodium formate (NaHCO2), a salt that is 100% dissociated in water. The Na+ ion is a Group IA cation and so gives a neutral solution. The formate ion, however, is the conjugate base of a weak acid (Table 16.2), so the solution is basic.
Step by Step Answer:

Chemistry And Chemical Reactivity
ISBN: 9780357001172
10th Edition
Authors: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel





