Lightning is a rapid transfer of charge from a cloud to the ground (or other parts of
Question:
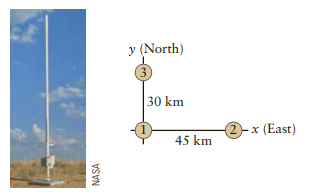
Lightning is a rapid transfer of charge from a cloud to the ground (or other parts of the cloud) and constitutes a very large, varying current. When a lightning strike occurs, a large pulse of electromagnetic radiation propagates outward in a wide range of frequencies from light waves to radio waves. NASA has developed a system called LDAR that is implemented near Cape Canaveral to monitor the sometimes sudden and dangerous lightning storms that pass through Florida. The difference in time of arrival of these radio waves is used in trilateration (“triangulation”) to measure the position of a lightning strike. Consider three antennas arranged in a right triangle formation as shown in Figure P23.56. Each antenna can pick up a radio pulse from as far away as 100 km. Placing antenna 1 at the origin, find the x and y coordinates of a lightning strike given the following travel times to antennas 1, 2, and 3: 93 μs, 131 μs, and 51 μs, respectively.
Figure P23.56
Step by Step Answer:

College Physics Reasoning and Relationships
ISBN: 978-0840058195
2nd edition
Authors: Nicholas Giordano





