The efficiency of typical power supply units (PSUs) varies as the load changes; for example, PSU efficiency
Question:
The efficiency of typical power supply units (PSUs) varies as the load changes; for example, PSU efficiency can be about 80% at 40% load (e.g., output 40 W from a 100-W PSU), 75% when the load is between 20% and 40%, and 65% when the load is below 20%.
a. Assume a power-proportional server whose actual power is proportional to CPU utilization, with a utilization curve as shown in Figure 6.3. What is the average PSU efficiency?
b. Suppose the server employs 2 N redundancy for PSUs (i.e., doubles the number of PSUs) to ensure stable power when one PSU fails. What is the average PSU efficiency?
c. Blade server vendors use a shared pool of PSUs not only to provide redundancy but also to dynamically match the number of PSUs to the server’s actual power consumption. The HP c7000 enclosure uses up to six PSUs for a total of 16 servers. In this case, what is the average PSU efficiency for the enclosure of server with the same utilization curve?
Figure 6.3
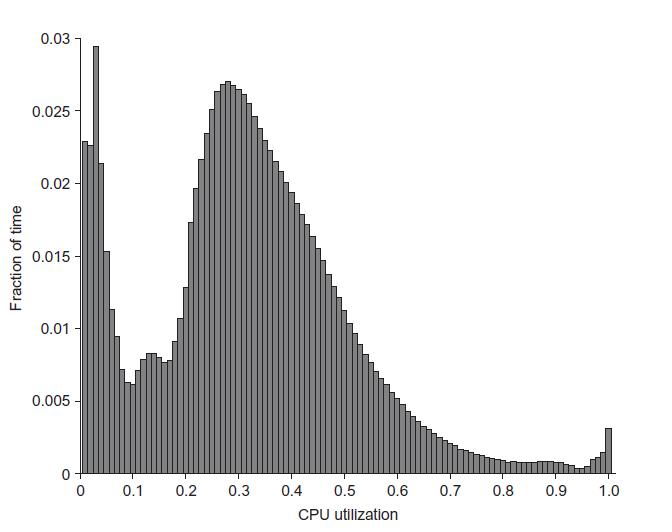
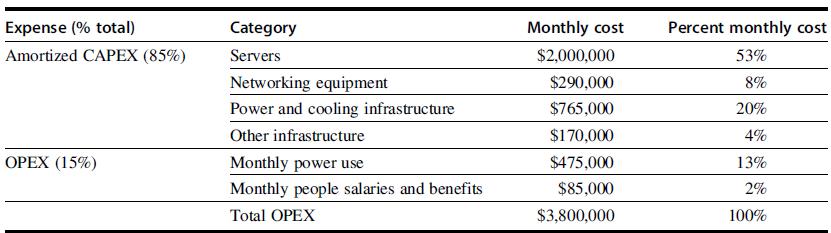
d. Consider the impact of the different efficiency numbers in the context of the broader TCO discussions in Figures 6.13 and 6.14: how do the different design impact the total TCO? Given these, how would you optimize designs for future warehouse-scale computers?
Figure 6.13
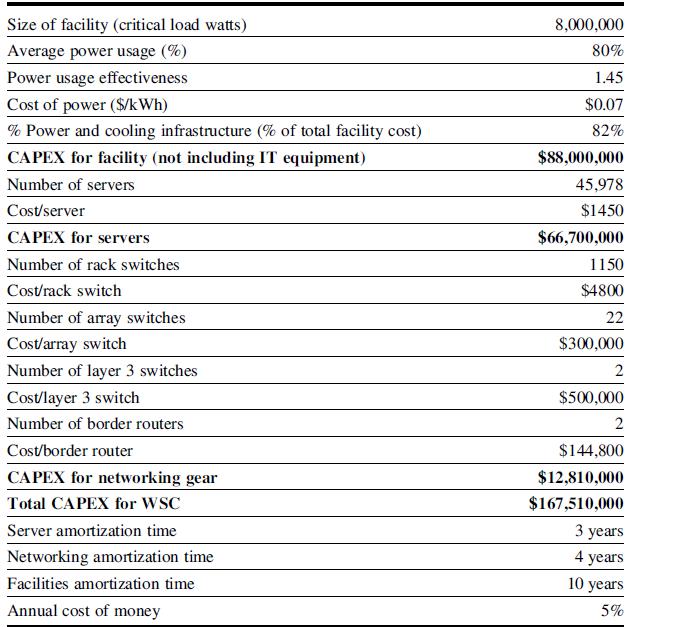
Figure 6.14
Step by Step Answer:

Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach
ISBN: 9780128119051
6th Edition
Authors: John L. Hennessy, David A. Patterson





