Outreach Explorations and Summit Adventures are the only two vacation adventure companies operating in a national park.
Question:
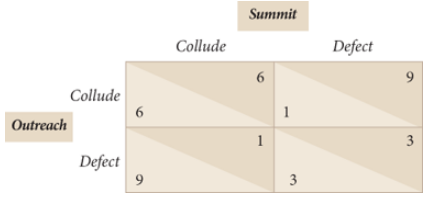
These firms compete with each other for five periods.
a. Summit follows a tit-for-tat strategy: It chooses the collusive price in the first period and in each later period chooses whichever action (collude or defect) that Outreach chose in the previous period. Create an Excel spreadsheet that shows Outreach€™s profit on a period by period basis as follows. Column A shows the time periods. Enter 1 in cell A2, 2 in cell A3 and so on up to 5 in cell A6. In cells B1 to F1 enter the column titles Strategy 1, . . . , Strategy 5. In column B, enter Outreach€™s profit each period if it chooses the collusive price each period. In Column C, assume that Outreach defects in each period. In Column D, assume that Outreach defects in the first period then plays the collusive price in each subsequent period. In Column E, assume that Outreach colludes for the first 4 periods then defects in the last period. In column F, assume that Outreach plays a tit-for-tat strategy. If Outreach wants to maximize its combined profit over all 5 periods, which of the 5 strategies is the best response to Summit€™s tit-for-tat strategy? Which is the worst?
b. Is the combination of strategies identified in part a (the tit-for-tat strategy by Summit and the best response by Outreach) a Nash equilibrium? (Hint: Create a new block of entries in your spreadsheet in which you assume that Outreach chooses the best response determined in part a. Enter the profits earned by Summit if it uses the tit-for-tat strategy and see if you can find a strategy that yields a higher cumulative profit for Summit over the 5 periods.)
c. Is it a Nash equilibrium in this game if each firm defects every period? Would your answer change if the game was repeated indefinitely instead of lasting only 5 periods.
Step by Step Answer:

Managerial Economics and Strategy
ISBN: 978-0134167879
2nd edition
Authors: Jeffrey M. Perloff, James A. Brander





