A heat exchanger is being designed as a component of a geothermal power system in which heat
Question:
A heat exchanger is being designed as a component of a geothermal power system in which heat is transferred from the geothermal brine to a “clean” fluid in a closed-loop power cycle. The heat exchanger, a shell-and-tube type, consists of 100 galvanized iron tubes 2 cm in diameter and 5 m long, as shown. The temperature of the fluid is 200°C, the density is 860 kg/m3, and the viscosity is 1.35 × l0–4 N∙s/m2. The total mass flow rate through the exchanger is 40 kg/s.
a. Calculate the power required to operate the heat exchanger, neglecting entrance and outlet losses.
b. After continued use, 2 mm of scale develops on the inside surfaces of the tubes. This scale has an equivalent roughness of 0.5 mm. Calculate the power required under these conditions.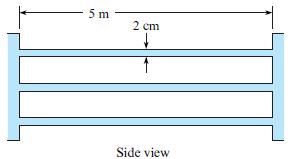
Step by Step Answer:

Engineering Fluid Mechanics
ISBN: 9781118880685
11th Edition
Authors: Donald F. Elger, Barbara A. LeBret, Clayton T. Crowe, John A. Robertson





