The enzyme carbonic anhydrase is one of the speediest enzymes known. It catalyzes the rapid conversion of
Question:
The enzyme carbonic anhydrase is one of the speediest enzymes known. It catalyzes the rapid conversion of CO2 gas into the much more soluble bicarbonate ion (HCO3–). The reaction: CO2 + H2O ↔ HCO3-+ H+ is very important for the efficient transport of CO2 from tissues, where CO2 is produced by respiration, to the lungs, where it is exhaled. Carbonic anhydrase accelerates the reaction 107-fold, hydrating 105 CO2 molecules per second at its maximal speed. What do you suppose limits the speed of the enzyme? Sketch a diagram analogous to the one shown in Figure 3−13 and indicate which portion of your diagram has been designed to display the 107-fold acceleration.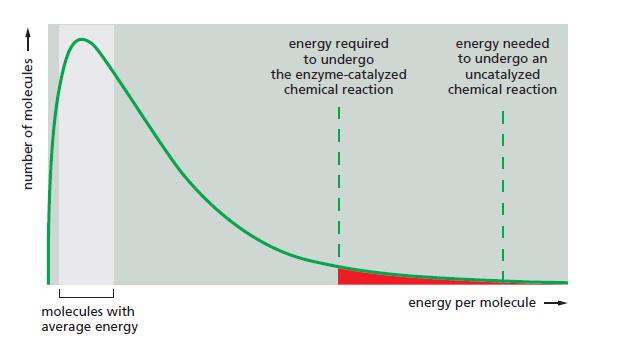
Step by Step Answer:

Essential Cell Biology
ISBN: 9780393680362
5th Edition
Authors: Bruce Alberts, Karen Hopkin, Alexander Johnson, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter





