Betty Simmons, the new financial manager of Southeast Chemicals (SEC), a Georgia producer of specialized chemicals for
Question:
Betty Simmons, the new financial manager of Southeast Chemicals (SEC), a Georgia producer of specialized chemicals for use in fruit orchards, must prepare a financial forecast for 2008. SEC's 2007 sales were $2 billion, and the marketing department is forecasting a 25% increase for 2008. Simmons thinks the company was operating at full capacity in 2007, but she is not sure about this. The 2007 financial statements, plus some other data, are shown below.
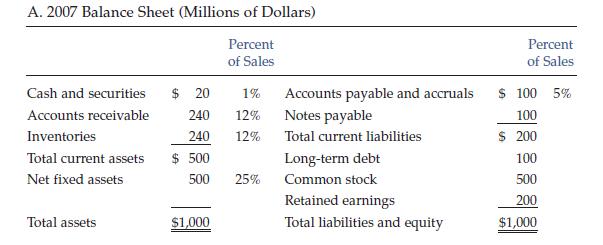
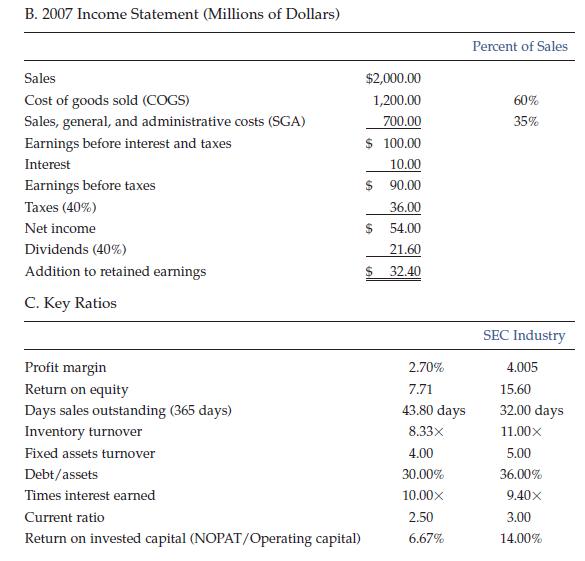
Assume that you were recently hired as Simmons's assistant, and your first major task is to help her develop the forecast. She asked you to begin by answering the following set of questions.
a. Describe three ways that pro forma statements are used in financial planning.
b. Explain the steps in financial forecasting.
c. Assume (1) that SEC was operating at full capacity in 2007 with respect to all assets, (2) that all assets must grow proportionally with sales, (3) that accounts payable and accruals will also grow in proportion to sales, and (4) that the 2007 profit margin and dividend payout will be maintained. Under these conditions, what will the company's financial requirements be for the coming year? Use the AFN equation to answer this question.
d. How would changes in the following items affect the AFN? (1) Sales increase;
(2) the dividend payout ratio increases; (3) the profit margin increases; (4) the capital intensity ratio increases; (5) SEC begins paying its suppliers sooner.
(Consider each item separately and hold all other things constant.)
e. Briefly explain how to forecast financial statements using the forecasted financial statements approach. Be sure to explain how to forecast interest expenses.
f. Now estimate the 2008 financial requirements using the forecasted financial statements approach. Assume (1) that each type of asset, as well as payables, accruals, and fixed and variable costs, will be the same percent of sales in 2008 as in 2007; (2) that the payout ratio is held constant at 40%; (3) that external funds needed are financed 50% by notes payable and 50% by long-term debt (no new common stock will be issued); (4) that all debt carries an interest rate of 10%; and (5) that interest expenses should be based on the balance of debt at the beginning of the year.
g. Why does the forecasted financial statements approach produce somewhat different AFN than the equation approach? Which method provides the more accurate forecast?
h. Calculate SEC's forecasted ratios, and compare them with the company's 2007 ratios and with the industry averages. Calculate SEC's forecasted free cash flow and return on invested capital (ROIC).
i. Based on comparisons between SEC's days sales outstanding (DSO) and inventory turnover ratios with the industry average figures, does it appear that SEC is operating efficiently with respect to its inventory and accounts receivable? Suppose SEC were able to bring these ratios into line with the industry averages and reduce its SGA/Sales ratio to 33%. What effect would this have on its AFN and its financial ratios? What effect would this have on free cash flow and ROIC?
j. Suppose you now learn that SEC's 2007 receivables and inventories were in line with required levels, given the firm's credit and inventory policies, but that excess capacity existed with regard to fixed assets. Specifically, fixed assets were operated at only 75% of capacity.
(1) What level of sales could have existed in 2007 with the available fixed assets? (2) How would the existence of excess capacity in fixed assets affect the additional funds needed during 2008?
k. The relationship between sales and the various types of assets is important in financial forecasting. The forecasted financial statements approach, under the assumption that each asset item grows at the same rate as sales, leads to an AFN forecast that is reasonably close to the forecast using the AFN equation.
Explain how each of the following factors would affect the accuracy of financial forecasts based on the AFN equation: (1) economies of scale in the use of assets and (2) lumpy assets.
Step by Step Answer:

Financial Management Theory & Practice
ISBN: 9780324652178
12th Edition
Authors: Eugene BrighamMichael Ehrhardt





