Combine your results from Prob. 4100 to form the two-dimensional strain rate tensor ij in the
Question:
Combine your results from Prob. 4–100 to form the two-dimensional strain rate tensor εij in the xy-plane,
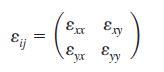
Are the x- and y-axes principal axes?
Data from Problem 100
For the two-dimensional Poiseuille flow of Prob. 4–99, calculate the linear strain rates in the x- and y-directions, and calculate the shear strain rate εxy.
Data from Problem 99
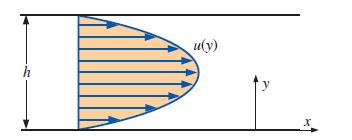
Consider fully developed two-dimensional Poiseuille flow—flow between two infinite parallel plates separated by distance h, with both the top plate and bottom plate stationary, and a forced pressure gradient dP/dx driving the flow as illustrated in Fig. P4–99. (dP/dx is constant and negative.)
The flow is steady, incompressible, and two-dimensional in the xy-plane. The velocity components are given by
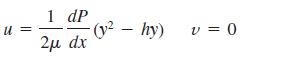
where μ is the fluid’s viscosity. Is this flow rotational or irrotational? If it is rotational, calculate the vorticity component in the z-direction. Do fluid particles in this flow rotate clockwise or counterclockwise?
Fig. P4–99.
Step by Step Answer:

Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9780073380322
3rd Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, John Cimbala





