Consider the garden hose nozzle of Probs. 929 and 965. Let the entrance and exit nozzle diameters
Question:
Consider the garden hose nozzle of Probs. 9–29 and 9–65. Let the entrance and exit nozzle diameters be 0.50 and 0.14 in, respectively, and let the nozzle length be 2.0 in. The volume flow rate through the nozzle is 2.0 gal/min.
(a) Calculate the axial speeds (ft/s) at the nozzle entrance and at the nozzle exit.
(b) Plot several streamlines in the rz-plane inside the nozzle, and design the appropriate nozzle shape.
Data from Problem 9–65
Consider the garden hose nozzle of Prob. 9–29. Generate an expression for the stream function corresponding to this flow field.
Data from Problem 9–29
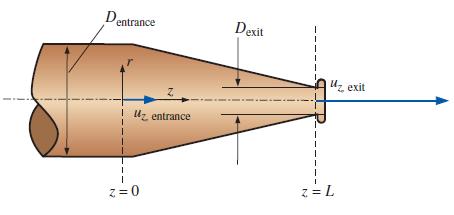
Consider steady flow of water through an axisymmetric garden hose nozzle (Fig. P9–29). The axial component of velocity increases linearly from uz, entrance to uz, exit as sketched. Between z = 0 and z = L, the axial velocity component is given by uz = uz,entrance + [(uz,exit – uz,entrance)/L]z. Generate an expression for the radial velocity component ur between z = 0 and z = L. You may ignore frictional effects on the walls.
Fig. P9–29
Step by Step Answer:

Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9780073380322
3rd Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, John Cimbala




