Question: In Chap. 9 (Example 915), we generated an exact solution of the NavierStokes equation for fully developed Couette flow between two horizontal flat plates (Fig.
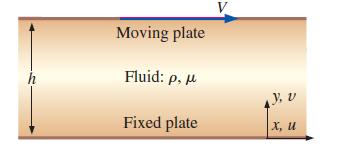
In Chap. 9 (Example 9–15), we generated an “exact” solution of the Navier–Stokes equation for fully developed Couette flow between two horizontal flat plates (Fig. P10–12), with gravity acting in the negative z-direction (into the page of Fig. P10–12). We used the actual pressure in that example. Repeat the solution for the x-component of velocity u and pressure P, but use the modified pressure in your equations. The pressure is P0 at z = 0. Show that you get the same result as previously. Discuss.
FIGURE P10–12
Data from Example 9-15
Consider steady, incompressible, laminar flow of a Newtonian fluid in the narrow gap between two infinite parallel plates (Fig. 9–57). The top plate is moving at speed V, and the bottom plate is stationary. The distance between these two plates is h, and gravity acts in the negative z-direction (into the page in Fig. 9–57). There is no applied pressure other than hydrostatic pressure due to gravity. This flow is called Couette flow. Calculate the velocity and pressure fields, and estimate the shear force per unit area acting on the bottom plate.
FIGURE 9–57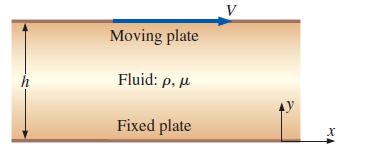
Moving plate Fluid: p, Fixed plate V AY, V X, U
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


