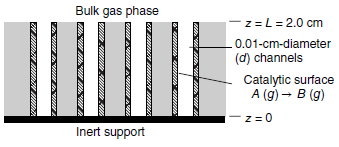
Consider one of the cylindrical channels of inner diameter d that run through an isomerization catalyst, as
Question:
n €“ C4H10 (g) †’ i €“ C4H10 (g)
The gas phase above the channels contains mixture of A and B maintained at a constant composition of 60 mol% A and 40 mol% B. Gas-phase species A diffuses down a straight channel of diameter d = 0.10 cm and length L = 2.0cm. The base of each channel is sealed. The surface reaction is rapid reaction so that the production rate of B is diffusion limited. The quiescent gas space in the channel consists of only species A and B.
a. State three relevant assumptions for the mass-transfer process. Based on your assumptions, simplify the general differential equation for the mass transfer of species A, leaving the differential equation in terms of the flux NA.
b. Simplify Fick€™s flux equation for each coordinate of interest, and then express the simplified form of general differential equation from part (a) above in terms of the gas-phase concentration cA.
c. Specify relevant boundary conditions for the gas-phase concentration cA.
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster





