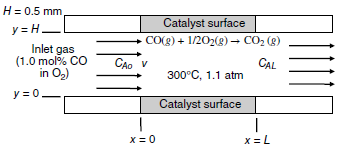
Consider the process shown in the figure below, where carbon monoxide (CO) gas is being oxidized to
Question:
a. Develop the final form of the general differential equation for mass transfer in terms of the concentration profile for CO, cA (species A). State all relevant assumptions, and also describe the source and sink for CO mass transfer.
b. State all necessary boundary conditions needed to specify the system.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster
Question Posted:





