Tubular membranes of silicone rubber can be used for bubble less aeration of water. A cross section
Question:
a. Develop an equation, in final integrated form, to predict the O2 flux across the tube wall from r = R1 to r = Ro, using C'A to describe the concentration of O2 dissolved in the tube wall material itself. State all assumptions. You may neglect convective mass-transfer resistances associated with the liquid boundary layer surrounding the tube.
b. At the conditions given above, determine the flux of oxygen to the water (r = Ro) if the well-mixed aqueous phase maintains the dissolved O2 concentration at 0.005 mole O2/m3.
Potentially useful data: The solubility of dissolved O2 in the silicone polymer is defined by a linear relationship pA = C'A/S, where PA is the partial pressure of O2 gas (atm), S is the solubility constant of O2 dissolved in the silicone polymer (S = 3.15 × 10-3 mmole O2/cm3 · atm at 25°C), and C'A is the concentration of O2 dissolved in the silicone rubber (mmol O2/cm3). The solubility of O2 gas in silicone rubber in contact with 2.0 atm O2 gas at 25°C is C'A* = 6.30 mole O2/m3 of silicone rubber. The Henry€™s law constant (H) of 0, in water is 078 atm · m3 water/gmole at 25°C. 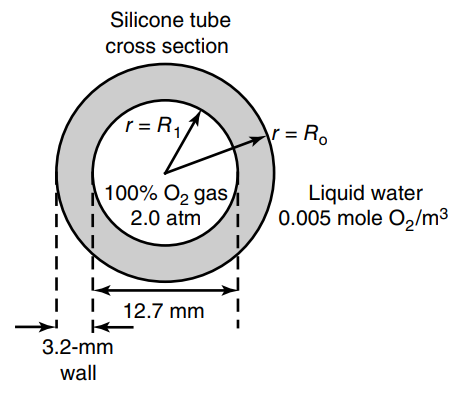
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster





