A treatise on atmospheric chemistry lists the following rate constants for the decomposition of PAN described in
Question:
A treatise on atmospheric chemistry lists the following rate constants for the decomposition of PAN described in the Integrative Example on page 965: 0 °C, k = 5.6 x 10-6 s-1; 10 °C, 3.2 x 10-5 s-1; 20 °C, 1.6 x 10-4 s-1; 30 °C, 7.6 x 10-4 s-1.
(a) Construct a graph of ln k versus 1/T.
(b) What is the activation energy, of the reaction?
(c) Calculate the half–life of the decomposition reaction at 40 °C.
Integrative Example
Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) is an air pollutant produced in photochemical smog by the reaction of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitrogen, and sunlight. PAN is unstable and dissociates into peroxyacetyl radicals and NO2(g). Its presence in polluted air is like a reservoir for NO2 storage.
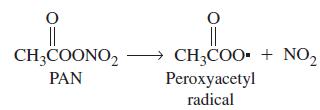
The first-order decomposition of PAN has a half-life of 35 hours at 0 °C and 30.0 min at 25 °C. At what temperature will a sample of air containing 5.0 x 1014 PAN molecules per liter decompose at the rate of 1.0 x 1012 PAN molecules per liter per minute?
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette




