Amino acids contain both an acidic carboxylic acid group (COOH) and a basic amino group (NH 2
Question:
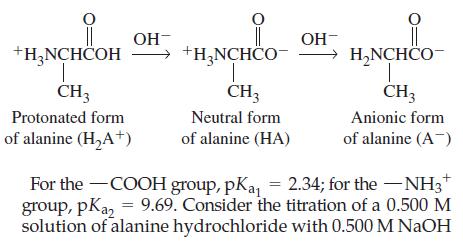
Amino acids contain both an acidic carboxylic acid group (—COOH) and a basic amino group (—NH2). The amino group can be protonated (that is, it has an extra proton attached) in a strongly acidic solution. This produces a diprotic acid of the form H2A+, as exemplified by the protonated amino acid alanine.
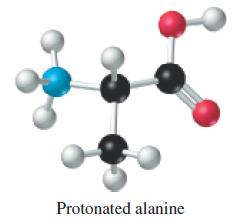
The protonated amino acid has two ionizable protons that can be titrated with OH-.
solution. What is the pH of
(a) The 0.500 M alanine hydrochloride;
(b) The solution at the first halfneutralization point;
(c) The solution at the first equivalence point? The dominant form of alanine present at the first equivalence point is electrically neutral despite the positive charge and negative charge it possesses. The point at which the neutral form is produced is called the isoelectric point. Confirm that the pH at the isoelectric point is
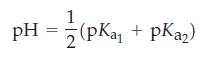
What is the pH of the solution
(d) Halfway between the first and second equivalence points?
(e) At the second equivalence point?
(f) Calculate the pH values of the solutions when the following volumes of the 0.500 M NaOH have been added to 50 mL of the 0.500 M alanine hydrochloride solution: 10.0 mL, 20.0 mL, 30.0 mL, 40.0 mL, 50.0 mL, 60.0 mL, 70.0 mL, 80.0 mL, 90.0 mL, 100.0 mL, and 110.0 mL.
(g) Sketch the titration curve for the 0.500 M solution of alanine hydrochloride, and label significant points on the curve.
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette




