Suppose you can bet on an American presidential election in which c of the candidates is an
Question:
Suppose you can bet on an American presidential election in which c of the candidates is an incumbent. The market offers you the following payoffs R
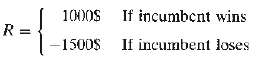
You can take either side of the bet Let the true probability of the incumbent winning be denoted by p. 0 (a) What is the expected gain if p =0.6? (b) Is the value of p important for you to make a decision on this bet?(c) Would two people taking this bet agree on their assessment of p? Which one would he correct? Can you tell?(d) Would statistical or econometric theory help in determining the p?(e) What weight would you put on the word of a statistician in making your decision about this bet?(F) How much would you pay for thisbet?
Step by Step Answer:

An Introduction to the Mathematics of financial Derivatives
ISBN: 978-0123846822
2nd Edition
Authors: Salih N. Neftci





