Resonance energy is the difference in energy between a real moleculea resonance hybridand its most important contributing
Question:
Resonance energy is the difference in energy between a real molecule—a resonance hybrid—and its most important contributing structure. To determine the resonance energy for benzene, we can determine an energy change for benzene and the corresponding change for one of the Kekulé structures. The resonance energy is the difference between these two quantities.
(a) Use data from Appendix D to determine the enthalpy of hydrogenation of liquid benzene to liquid cyclohexane.
(b) Use data from Appendix D to determine the enthalpy of hydrogenation of liquid cyclohexene to liquid cyclohexane.
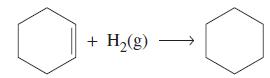
For the enthalpy of formation of liquid cyclohexene, use ΔfH ° = -38.5 kJ/mol.
(c) Assume that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of 1,3,5-cyclohexatriene is three times as great as that of cyclohexene, and calculate the resonance energy of benzene.
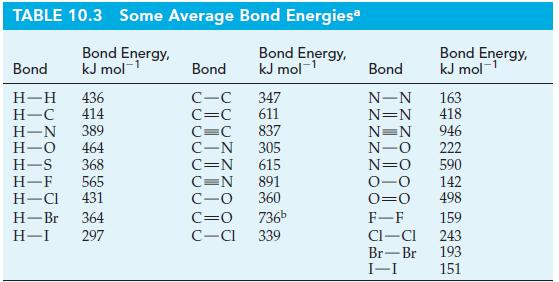
(d) Another way to assess resonance energy is through bond energies. Use bond energies from Table 10.3 (page 451) to determine the total enthalpy change required to break all the bonds in a Kekulé structure of benzene. Next, determine the enthalpy change for the dissociation of C6H6(g) into its gaseous atoms by using data from Table 10.3 and Appendix D. Then calculate the resonance energy of benzene.
Table 10.3
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette





