A method for determining the thermal conductivity (k) and the specific heat (c_{p}) of a material is
Question:
A method for determining the thermal conductivity \(k\) and the specific heat \(c_{p}\) of a material is illustrated in the sketch. Initially the two identical samples of diameter \(D=50 \mathrm{~mm}\) and thickness \(L=10 \mathrm{~mm}\) and the thin heater are at a uniform temperature of \(T_{i}=23.00^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), while surrounded by an insulating powder. Suddenly the heater is energized to provide a uniform heat flux \(q_{o}^{\prime \prime}\) on each of the sample interfaces, and the heat flux is maintained constant for a period of time, \(\Delta t_{0}\). A short time after sudden heating is initiated, the temperature at this interface \(T_{o}\) is related to the heat flux as
\[T_{o}(t)-T_{i}=2 q_{o}^{\prime \prime}\left(\frac{t}{\pi ho c_{p} k}\right)^{1 / 2}\]
For a particular test run, the electrical heater dissipates \(20.0 \mathrm{~W}\) for a period of \(\Delta t_{o}=100 \mathrm{~s}\), and the temperature at the interface is \(T_{o}(60 \mathrm{~s})=26.77^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) after \(60 \mathrm{~s}\) of heating. A long time after the heater is deenergized, \(t \gg \Delta t_{0}\), the samples reach the uniform temperature of \(T_{o}(\infty)=\) \(39.80^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The mass of each sample is \(m=78\) grams.
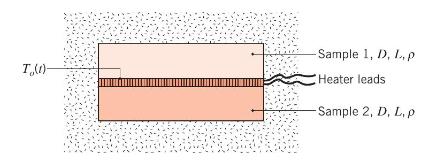
Determine the specific heat and thermal conductivity of the test material. By looking at values of the thermophysical properties in Table A. 1 or A.2, identify the test sample material.
Data From Table A.2:-
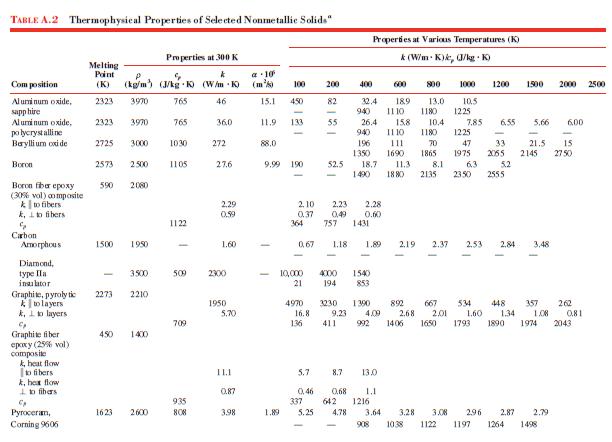
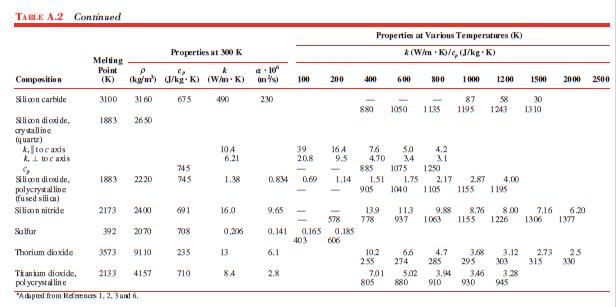
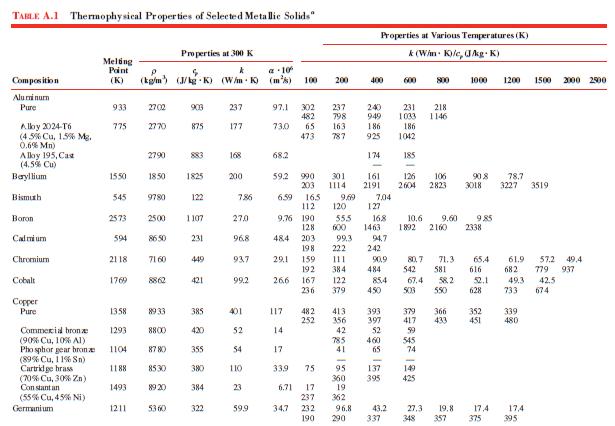
Data From Table A.1:-
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781119220442
8th Edition
Authors: Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine




