Consider a large plane wall of thickness L = 0.3 m, thermal conductivity k = 2.5 W/m
Question:
Consider a large plane wall of thickness L = 0.3 m, thermal conductivity k = 2.5 W/m · K, and surface area A = 12 m2. The left side of the wall at x = 0 is subjected to a net heat flux of q̇0 = 700 W/m2 while the temperature at that surface is measured to be T1 = 80°C. Assuming constant thermal conductivity and no heat generation in the wall,
(a) Express the differential equation and the boundary conditions for steady one-dimensional heat conduction through the wall,
(b) Obtain a relation for the variation of temperature in the wall by solving the differential equation,
(c) Evaluate the temperature of the right surface of the wall at x = L.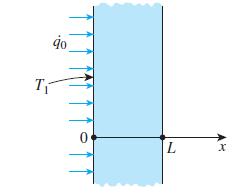
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Heat And Mass Transfer Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9780073398181
5th Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, Afshin Ghajar
Question Posted:





