Design a packed-bed air humidifier to process (9.12 mathrm{~kg} / mathrm{h}) of dry air. Assume that conditions
Question:
Design a packed-bed air humidifier to process \(9.12 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{h}\) of dry air. Assume that conditions are like those of Example 2.13. The packing will consist of spherical glass beads with a particle-to-bed diameter ratio of \(1 / 20\). The partial pressure of water in the outlet air must be \(99.9 \%\) of the maximum and the total gas pressure drop is not to exceed \(500 \mathrm{~Pa}\). Assuming a cylindrical bed, determine the diameter and depth of the bed, the gas mass velocity, and the diameter of the glass beads.
Data From Example 2.13:-
The column of Example 2.12 is packed with spherical glass beads, with diameter of 3.5 mm. The water is now supplied as a fine mist that flows down through the packed bed at a flow rate just enough to replace the water lost by vaporization, and to keep the surface of the packing wet. Under these conditions, it may be assumed that equation (2-90) applies.
(a) Estimate the depth of packing required if the water partial pressure in the air leaving the bed is to be 99% of the water vapor pressure PA.
(b) Estimate the gas pressure drop through the bed.
Data From Example 2.12:-
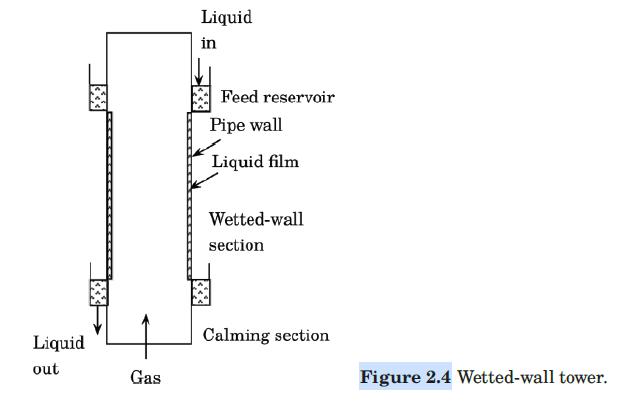
Water flows down the inside wall of a wetted-wall tower of the design of Figure 2.4, while air flows upward through the core. The ID of the tower is 25.4 mm, and the length of the wetted section is 1.5 m. Dry air enters the wetted section at a mass velocity of 5.0 kg/m2·s, a temperature of 308 K, and a pressure of 1 atm. The water enters at 295 K. Estimate the partial pressure of water in the air leaving the tower. Assume that the temperature of the air and of the water remain constant.
Figure 2.4:-
Data From Equation 2-90:-
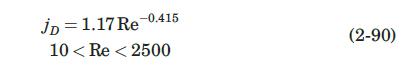
Step by Step Answer:






