Chemists and engineers must be able to predict the changes in chemical concentration in a reaction. A
Question:
Chemists and engineers must be able to predict the changes in chemical concentration in a reaction. A model used for many singlereactant processes is
Rate of change of concentration = -kCn
where C is the chemical concentration and k is the rate constant. The order of the reaction is the value of the exponent n. Solution methods for differential equations (which are discussed in Chapter 9) can show that the solution for a first-order reaction (n = 1) is
C(t) = C(0)e-kt
The solution for a second-order reaction (n = 2) is
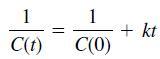
and the solution for a third-order reaction (n = 3) is
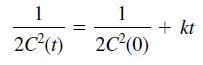
Time t (min) …………… C (mol of reactant/L)
5 …………………………………… 0.3575
10 ………………………………….. 0.3010
15 ………………………………….. 0.2505
20 ………………………………….. 0.2095
25 ………………………………….. 0.1800
30 ………………………………….. 0.1500
35 ………………………………….. 0.1245
40 ………………………………….. 0.1070
45 ………………………………….. 0.0865
The preceding data describe a certain reaction. By examining the residuals, determine whether this is a first-order , second-order, or third-order reaction, and estimate the value of the rate constant k.
Step by Step Answer:






