A nominal 12 hp electric sump pump for household use comes with the following data: where GPM
Question:
A nominal 1⁄2 hp electric sump pump for household use comes with the following data: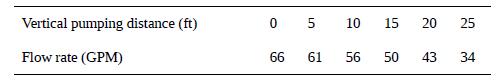
where GPM is gallons per minute. A typical installation is shown in Fig. P11.14. The average water depth at the intake is h and the discharge is through a pipe of diameter D at a height H and mean velocity v. It is desired to estimate the efficiency of the pump from these data. Although the details of the test setup were not provided, the threaded fitting on the pump suggests that the pipe might have been 1 1⁄2″ Schedule 40 PVC (D = 4.04 cm). Assume that the pipe length equaled the height H.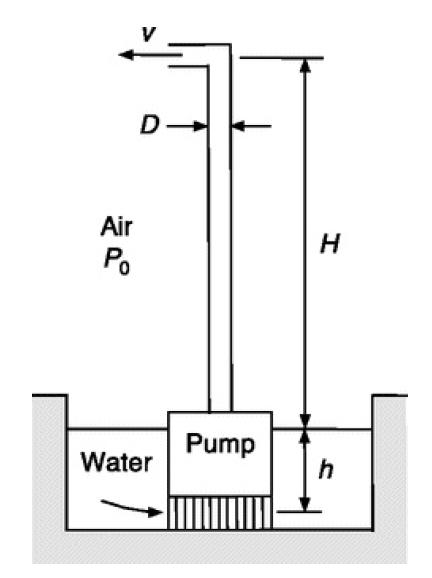
![]()
(a) Confirm that the flow was turbulent under all conditions tested and find the range of values of the friction factor. The range of f is small enough that an average value can be used subsequently.
(b) Relate Wm to H, Q, and the various constants (including f). You may neglect the kinetic energy at the pump intake and consider viscous losses only in the pipe.
(c) Use the data to calculate Wm as a function of H for H ≥ 5 ft. [Why should the results for H = 0 not be used?] Find the nominal efficiency of the pump, which is Wm divided by the rated 1⁄2 hp. To obtain a true efficiency (Wm relative to the electric power used), we would need to know how much current was actually drawn during the tests.
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics
ISBN: 9781107123779
1st Edition
Authors: William M. Deen





