It is desired to infer the value of the loss coefficient of the valvespigot combination in a
Question:
It is desired to infer the value of the loss coefficient of the valve–spigot combination in a household bathtub. As shown in Fig. P12.7, leading from the underground water main to the house is pipe of diameter D1 and total length L1, with one 90° bend. Inside the house are pipe segments of diameter D2 and total length L2. The interior pipe leading to the tub has seven 90° bends and an open gate valve. There is a total rise H from water main to tub spigot. The main and atmospheric pressures are Pm and P0, respectively.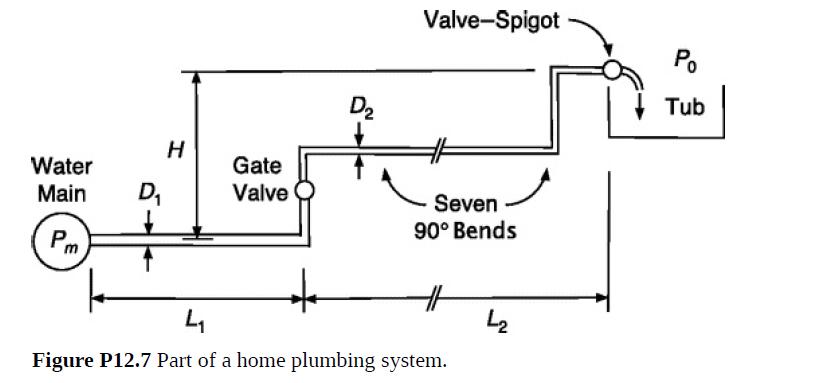
Water is supplied at a gauge pressure Pm − P0 = 2.4 × 105 Pa. All of the pipe is copper. The 3⁄4-inch exterior pipe has a length L1 = 20 m and actual diameter D1 = 1.9 cm. The 1⁄2-inch interior pipe has a length L2 = 16 m and actual diameter D2 = 1.4 cm. The rise is H = 4 m and the spigot diameter is approximately 2 cm. If the flow rate at 20 °C is 1.9 × 10–4 m3/s when the tub valve is opened, what is the valve–spigot loss coefficient?
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics
ISBN: 9781107123779
1st Edition
Authors: William M. Deen





