Consider the economy described in Problem 4. a. Construct real GDP for years 2012 and 2013 by
Question:
Consider the economy described in Problem 4.
a. Construct real GDP for years 2012 and 2013 by using the average price of each good over the two years.
b. By what percentage does real GDP change from 2012 to 2013?
c. What is the GDP deflator in 2012 and 2013? Using the GDP deflator, what is the rate of inflation from 2012 to 2013?
d. Is this an attractive solution to the problems pointed out in Problems 4 and 5 (i.e., two different growth rates and two different inflation rates, depending on which set of prices is used)? (The answer is yes and is the basis for the construction of chained-type deflators. See the appendix to this chapter for more discussion.)
An economy produces three goods: cars, computers, and oranges.
Quantities and prices per unit for years 2012 and 2013 are as follows:
Data from Problem 4
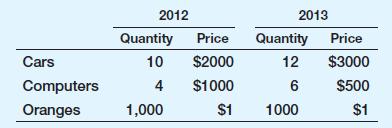
a. What is nominal GDP in 2012 and in 2013? By what percentage does nominal GDP change from 2012 to 2013?
b. Using the prices for 2012 as the set of common prices, what is real GDP in 2012 and in 2013? By what percentage does real GDP change from 2012 to 2013?
c. Using the prices for 2013 as the set of common prices, what is real GDP in 2012 and in 2013? By what percentage does real GDP change from 2012 to 2013?
d. Why are the two output growth rates constructed in parts b and c different? Which one is correct? Explain your answer.
Step by Step Answer:






