Intermediate: Interpretation of variances and calculation of materials, labour and sales variances. Sticky Wicket (SW) manufactures cricket
Question:
Intermediate: Interpretation of variances and calculation of materials, labour and sales variances.
Sticky Wicket (SW) manufactures cricket bats using high quality wood and skilled labour using mainly traditional manual techniques. The manufacturing department is a cost centre within the business and operates a standard costing system based on marginal costs.
At the beginning of April the production director attempted to reduce the cost of the bats by sourcing wood from a new supplier and deskilling the process a little by using lower grade staff on parts of the production process. The standards were not adjusted to reflect these changes.
The variance report for April is shown below (extract):

The production director pointed out in his April board report that the new grade of labour required significant training in April and this meant that productive time was lower than usual. He accepted that the workers were a little slow at the moment but expected that an improvement would be seen in May. He also mentioned that the new wood being used was proving difficult to cut cleanly resulting in increased waste levels.
Sales for April were down 10 per cent on budget and returns of faulty bats were up 20 per cent on the previous month. The sales director resigned after the board meeting stating that SW had always produced quality products but the new strategy was bound to upset customers and damage the brand of the business.
Required
(a) Assess the performance of the production director using all the information above taking into account both the decision to use a new supplier and the decision to deskill the process. (7 marks)
In May the budgeted sales were 19000 bats and the standard cost card is as follows:

In May the following results were achieved:
40 000kg of wood were bought at a cost of $196 000, this produced.19 200 cricket bats. No inventory of raw materials is held. The labour was paid for 62000 hours and the total cost was $694 000. Labour worked for 61.500 hours.
The sales price was reduced to protect the sales levels. However, only 18000 cricket bats were sold at an average price of $65.
Required: ae .
(bb) Calculate the materials, labour and sales variances for May in as much detail as the information allows.You are not required to comment on the performance of the business.
' (13 marks)
ACCA F5 Performance Management17.19 Intermediate: Variable costing reconciliation statement.
HB makes and sells a single product. The company operates a standard marginal costing system and a just-in-time purchasing and production system. No inventory of raw materials or finished goods is held.
Details of the budget and actual data for the previous period are given below:
Budget data Standard production costs per unit:
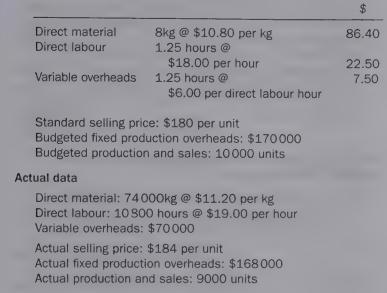
Required:
(a) Prepare a statement using marginal costing principles that reconciles the budgeted profit and the actual profit. Your statement should show the variances in as much detail as possible. (11 marks)
(2) (i) Explain why the variances used to reconcile profit in a standard marginal casting system are different from those used in a standard absorption costing system.
(4 marks)
(ji) Calculate the variances that would be different and any additional variances that would be required if the reconciliation statement was prepared using standard absorption costing.
Note: Preparation of a revised statement is not required.
(4 marks)
(ce) Explain the arguments for the use of traditional absorption costing rather than marginal costing for profit reporting and inventory valuation. (6 marks)
CIMA Performance Operations
Step by Step Answer:






