Exercise 7 Pulse Rates Refer to the exercise identified. Make subjective estimates to decide whether results are
Question:
Exercise 7 “Pulse Rates”
Refer to the exercise identified. Make subjective estimates to decide whether results are significantly low or significantly high, then state a conclusion about the original claim. For example, if the claim is that a coin favors heads and sample results consist of 11 heads in 20 flips, conclude that there is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the coin favors heads (because it is easy to get 11 heads in 20 flips by chance with a fair coin).
Data From Exercise 7:
Claim: The mean pulse rate (in beats per minute, or bpm) of adult males is equal to 69 bpm. For the random sample of 153 adult males in Data Set 1 “Body Data” in Appendix B, the mean pulse rate is 69.6 bpm and the standard deviation is 11.3 bpm.
Do the following:
a. Express the original claim in symbolic form.
b. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses.
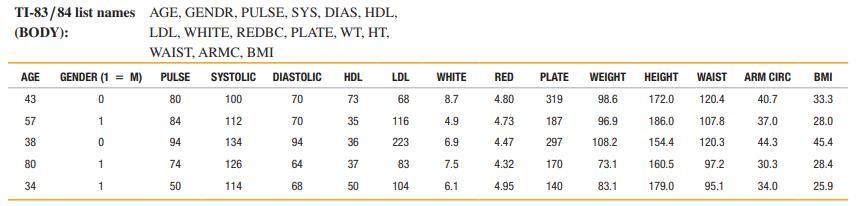
Data Set 1: Body Data
Body and exam measurements are from 300 subjects (first five rows shown here). AGE is in years, for GENDER 1 = male and 0 = female, PULSE is pulse rate (beats per minute), SYSTOLIC is systolic blood pressure (mm Hg), DIASTOLIC is diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg), HDL is HDL cholesterol (mg/dL), LDL is LDL cholesterol (mg/dL), WHITE is white blood cell count (1000 cells/mL), RED is red blood cell count (million cells/mL), PLATE is platelet count (1000 cells/mL), WEIGHT is weight (kg), HEIGHT is height (cm), WAIST is waist circumference (cm), ARM CIRC is arm circumference (cm), and BMI is body mass index (kg/m2). Data are from the National Center for Health Statistics.
Step by Step Answer:

Mathematical Interest Theory
ISBN: 9781470465681
3rd Edition
Authors: Leslie Jane, James Daniel, Federer Vaaler





