A holographic lens, like any other hologram, can be described by its transmissivity t(x, y). (a) What
Question:
A holographic lens, like any other hologram, can be described by its transmissivity t(x, y).
(a) What t(x, y) will take a reference wave, impinging from the θo direction (as in Fig. 10.8) and produce from it a primary object wave that converges on the spot (x, y, z) = (0, 0, d)?
(b) Draw a contour plot of the transmissivity t(x, y) of the lens in part (a). Notice the resemblance to the Fresnel zone plate of Sec. 8.4.4. Explain the connection of the two, paying attention to how the holographic lens changes when one alters the chosen angle θo of the reference wave.
(c) What t(x, y) will take a reference wave, impinging from the θo direction, and produce from it a primary wave that splits in two, with equal light powers converging on the spots (x, y, z) = (−a, 0, d) and (x, y, z) = (+a, 0, d)?
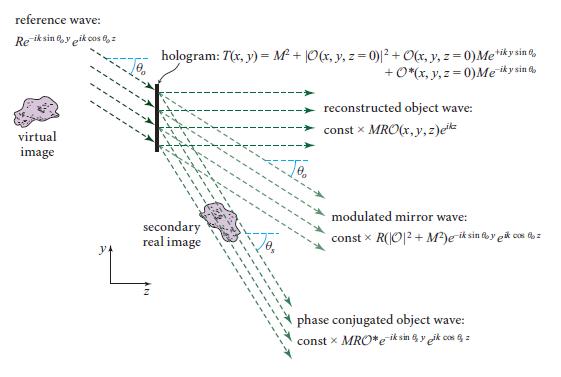
Figure 10.8.
Step by Step Answer:

Modern Classical Physics Optics Fluids Plasmas Elasticity Relativity And Statistical Physics
ISBN: 9780691159027
1st Edition
Authors: Kip S. Thorne, Roger D. Blandford




