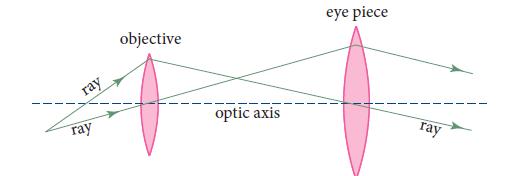
A microscope takes light rays from a point on a microscopic object, very near the optic axis,
Question:
A microscope takes light rays from a point on a microscopic object, very near the optic axis, and transforms them into parallel light rays that will be focused by a human eye’s lens onto the eye’s retina (Fig. 7.8). Use matrix methods to explore the operation of such a microscope. A single lens (magnifying glass) could do the same job (rays from a point converted to parallel rays). Why does a microscope need two lenses? What focal lengths and lens separations are appropriate for the eye to resolve a bacterium 100 μm in size?
Fig. 7.8.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Modern Classical Physics Optics Fluids Plasmas Elasticity Relativity And Statistical Physics
ISBN: 9780691159027
1st Edition
Authors: Kip S. Thorne, Roger D. Blandford
Question Posted:





