An external magnetic field B0 can cause the straight-line path of a laser beam to deflect inside
Question:
An external magnetic field B0 can cause the straight-line path of a laser beam to deflect inside a non-simple material where the constitutive relations are B = μH and D = εE − iγB × E. To see this, let a linearly polarized, monochromatic plane wave with electric field strength E enter the material at normal incidence. Assume that B0 lies in a plane perpendicular to the propagation vector k and makes an angle ϕ with D.
(a) Use explicit numerical estimates to show that the typical value of B0 produced by a laboratory electromagnet is much larger than the magnetic field associated with, e.g., a continuous-wave argon-ion laser beam.
(b) To lowest order in B0, show that the time-averaged Poynting vector inside the material is
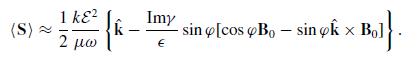
(c) What angle of ϕ produces maximum deflection?
Step by Step Answer:






