Amide A, -valerolactam, is a typical amide with a conjugate-acid pK a of 0.8. The two cyclictertiary
Question:
Amide A, δ-valerolactam, is a typical amide with a conjugate-acid pKa of 0.8. The two cyclic tertiary amines B and C also have typical conjugate-acid pKa values. In contrast, the conjugate-acid pKa of amide D is unusually high for an amide, and it hydrolyzes much more rapidly than other amides. Draw the structure of the conjugate acid of amide D, and suggest a reason for both its unusual pKa and its rapid hydrolysis.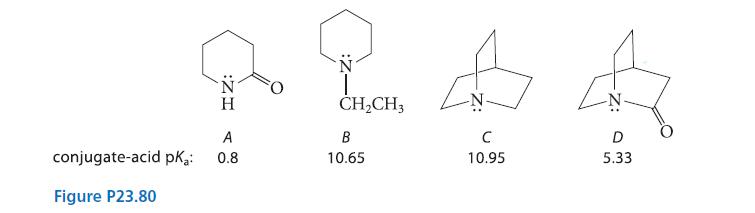
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





