The enzyme dehydroquinate synthase catalyzes reactions (1) and (3) in the sequence shown in Fig. P22.97, which
Question:
The enzyme dehydroquinate synthase catalyzes reactions (1) and (3) in the sequence shown in Fig. P22.97, which is part of the pathway for the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids such as tryptophan; reactions (2), (4), and (5) occur spontaneously.
(a) Assuming that acids and bases are present as needed, propose a curved-arrow mechanism for reaction (2). To what laboratory reaction is this reaction analogous?
(b) The two enzyme-catalyzed steps (1) and (3) are, respectively, an oxidation and a reduction that consume and then regenerate an NAD+ and result in no net change at the carbon involved. What is the chemical rationale for these two reactions?
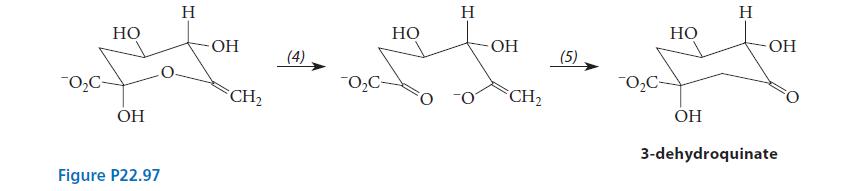
(c) Assuming that acids and bases are present as needed, propose curved-arrow mechanisms for reactions (4) and (5). To what laboratory reactions are these similar?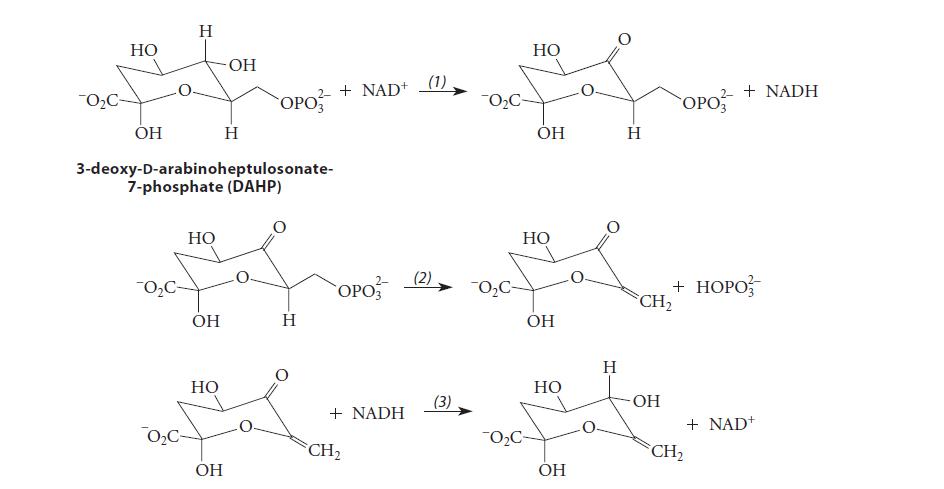
Step by Step Answer:






