When acetoacetic acid is decarboxylated in the presence of bromine, bromoacetone is isolated (see Fig. P22.68). The
Question:
When acetoacetic acid is decarboxylated in the presence of bromine, bromoacetone is isolated (see Fig. P22.68).
The rate of appearance of bromoacetone is described by the following rate law:![]()
(The reaction rate is zero order in bromine.) Suggest a mechanism for the reaction that is consistent with this rate law.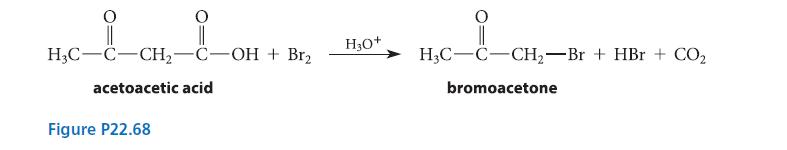
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





