When S-ethyl thiobenzoate (A) is allowed to react with 2-aminoethanol (B), an amide C is formed if
Question:
When S-ethyl thiobenzoate (A) is allowed to react with 2-aminoethanol (B), an amide C is formed if one equivalent of triethylamine (Et3N:) is included in the reaction mixture, but an ester D is formed if one equivalent of a strong acid such as p-toluenesulfonic acid is added as a catalyst. (See Fig. P25.25.) Give the structures of C and D, and explain why different products are formed under different conditions.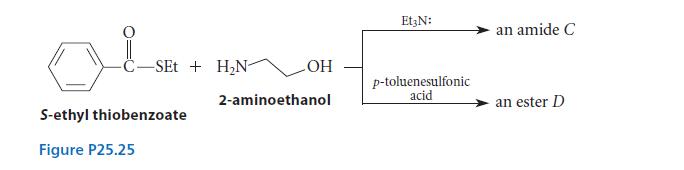
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





