Question: In the previous problem, we saw that an acetylide ion can attack a variety of electrophiles. In Chapter 20, we will see that a C=O
In the previous problem, we saw that an acetylide ion can attack a variety of electrophiles. In Chapter 20, we will see that a C=O bond can also function as an electrophile. Consider the following reaction between an acetylide ion (the nucleophile) and a ketone (the electrophile):
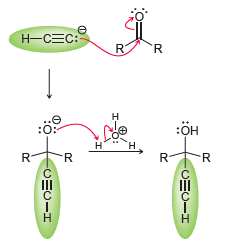
The acetylide ion attacks the ketone, generating an alkoxide ion. After the reaction is complete, a proton source is used to protonate the alkoxide ion. In a synthesis, these two steps must be shown separately, because the acetylide ion will not survive in the presence of H3O+. Using this information, propose a plausible synthesis for allyl alcohol, using acetylene as your only source of carbon atoms:
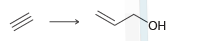
-: 'R : R- -R R- R
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
H Lindlars Catalys... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


